File-Based Primary Storage Ransomware Protection
Fast movers being Ctera, RackTop, Infinidat, Cohesity, and NetApp
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on September 11, 2023 at 2:02 pmPublished on August 23, 2023, this market report was written by independant analysts Arjan Timmerman and Max Mortillaro for GigaOm.
GigaOm Sonar Report for File-Based Primary Storage Ransomware Protectionv2.0
An Exploration of Cutting-Edge Solutions and Technologies
1. Summary
Ransomware is a specific type of malware that encrypts data assets on primary storage systems – including file shares, databases, disk partitions, data volumes, backup systems, and repositories – making them inaccessible unless the victim pays an extortion fee. Ransomware is highly optimized to spread across organizations via networks and infrastructure systems through methods similar to Trojan malware attacks. The ransomware payload is embedded in a file that looks legitimate and is triggered by an unsuspecting user opening the infected file. Usually, it will spread across the environment by taking advantage of user credentials, along with documented and undocumented exploits, bypassing the limited access scope of a user. Thus, ransomware protection is a transversal, cross-stack topic of discussion across organizations.
Ransomware attacks can impact file- and block-based primary storage solutions alike:
- File-based ransomware attacks are the most pervasive. Advanced file-based ransomware implementations use a combination of techniques to remain unnoticed and spread silently. For example, they may start encryption activities a few weeks or months after a system has been infiltrated, or they may first target dormant files that haven’t been accessed for a long time.
- Block-based ransomware attacks, while less common, can be even more damaging. Ransomware encrypts entire data volumes, making recovery much harder than for file-based attacks. The entire volume must be recovered, which offers less granularity and fewer recovery prioritization options than for file-based recovery activities. These attacks, however, are quicker and easier to detect because once a volume is encrypted, all R/W operations become impossible.
One Sonar report focuses on ransomware protection solutions available for file-based – or NAS – primary storage systems; a sister report covers solutions for block-based primary storage.
Figure 1. Vendors Included in Each GigaOm Sonar for Primary Storage Ransomware Protection
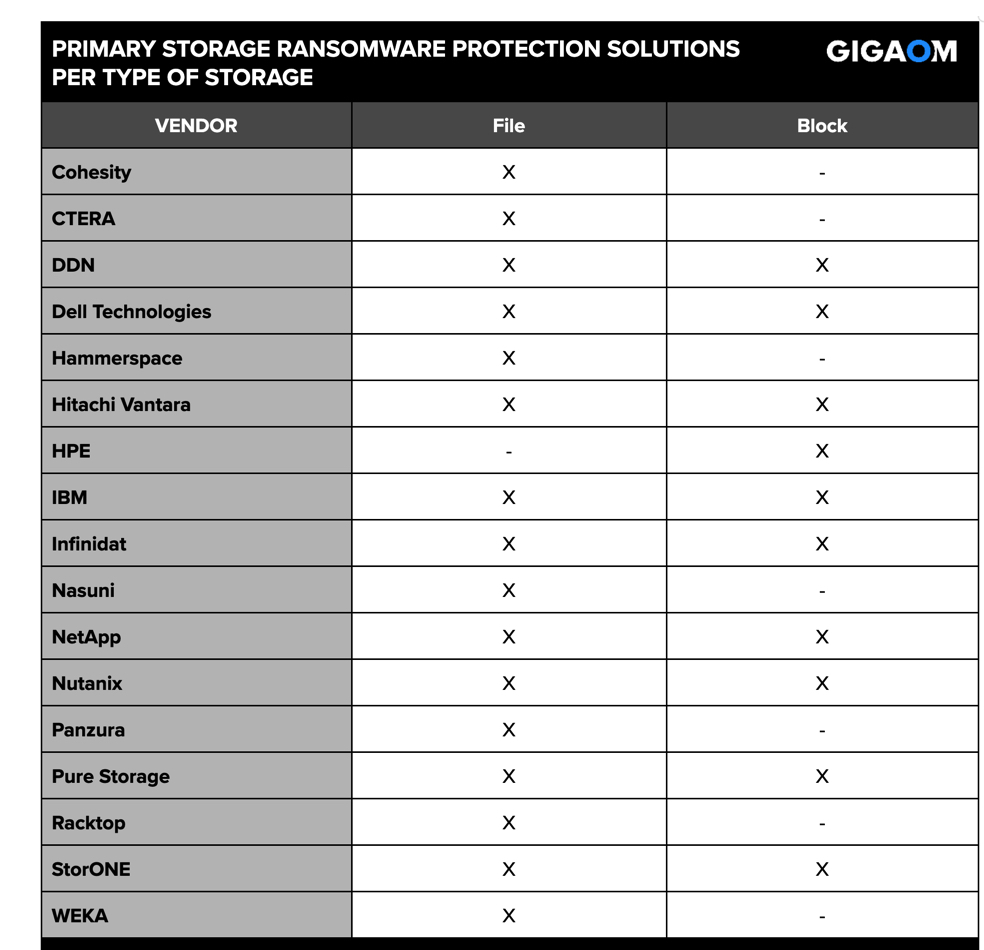
Although dedicated out-of-band ransomware protection solutions exist, organizations should not underestimate the benefits of in-band ransomware protection capabilities embedded in NAS and block-based solutions. The most effective mitigations include a combination of in-band and out-of-band capabilities, but for smaller businesses or very cost-conscious organizations, NAS and block-based ransomware protection solutions constitute an important first line of defense.
Benefits of ransomware protection on NAS and block-based solutions include:
- Faster recovery from a ransomware attack than backup restores can provide, usually measured in minutes instead of hours or days, thanks to snapshots. This quick recovery is particularly crucial for mission-critical applications that can’t withstand prolonged downtimes.
- Greater ease of use delivered because reverting to a healthy snapshot takes considerably less effort than identifying and orchestrating data recovery from a data protection platform.
- Cost-effective protection and recovery operations: NAS and block-based ransomware protection solutions are usually provided at no cost and deliver a very effective protection layer. Furthermore, fast local recovery from ransomware using ransomware solutions is cheaper than recovery using data protection systems, from both an elapsed time and a human effort perspective. In addition, organizations avoid paying any potential egress transfer fees when restoring from the cloud.
These GigaOm Sonars provide an overview of file-based and block-based primary storage ransomware protection vendors and their available offerings, equipping IT decision-makers with the information they need to select the best solution for their business and use case requirements.
2. Overview
How We Got Here
Ransomware attacks have become a prevalent and persistent threat for organizations across all varieties and sizes of businesses. While these attacks made headlines a few years ago, they’ve now become so widespread that only the most spectacular cases are mentioned in the news media today.
Organizations assess business risk by evaluating the probability of an event occurring and correlating this probability with the extent of possible damage, usually through a risk assessment matrix. The impact can be diverse, ranging from negligible to widespread, but regardless of the physical manifestation, outcomes are generally summed up in three categories: financial (loss of revenue), regulatory (increased scrutiny, fines, and, eventually, the loss of license for regulated businesses), and reputational (loss of trust by customers).
Ransomware is particularly concerning for organizations because it combines a high probability of happening with a widespread impact, not only in terms of locations and systems affected but also in terms of damage. Ransomware can bring businesses and government agencies to their knees, forcing them to choose between paying a hefty ransom or the risk of losing production capacity and revenue for weeks, if not months.
Ransomware does not discriminate among infrastructure layers; once in, it attempts to encrypt all of an organization’s assets within reach, which is why proper segmentation of access and networks is important. Organizations usually implement several data protection layers, including backups and disaster recovery, security at the network layer, and authentication mechanisms that reduce the attack surface. However, relying solely on backups should be avoided for the following reasons:
Primary data is the most up-to-date data available in the organization. Large enterprises can have a significant delta between production data and data backups, especially if the data has elevated change rates.
Losing primary data and having to restore it from data protection platforms is a time-intensive process, limited by the throughput of the backup media and network bandwidth, especially if protected data resides on the cloud.
For cloud-based data protection, data retrieval could incur egress transfer fees, which can add up quickly as more data and systems need to be recovered.
Primary data is the first point of impact for ransomware attacks, so it’s advisable to implement primary storage solutions that incorporate ransomware protection. Timely identification, alerting, and mitigation are preferable to dealing with the aftermath of a ransomware attack and its severe financial, regulatory, and reputational impacts.
File-Based Primary Storage for Ransomware Protection
NAS systems are prone to ransomware attacks because they present all the characteristics that facilitate a ransomware attack:
- They are the primary point of storage for collaboration use cases broadly used by human operators within the organization.
- They are the primary storage target for many data asset types, regardless of their criticality.
- They typically involve shared storage, which is usually accessible by numerous individuals across many geographic locations.
- They hold a broad range of types and large numbers of files that are accessible by many individuals—and therefore accessible by any malicious process running on their endpoints.
Permissions may be lax or not required at all on certain shares and folders. - Without proper controls, such as segmentation of data, least-privilege access, and stringent permissions, file storage repositories become easy targets for the unchecked spread of ransomware.
Solution Components
The goal of ransomware protection on primary storage is to act as the 1st line of defense by mitigating threats and ensuring primary data remains protected, thereby ensuring continuity of operations. Primary storage solutions can provide ransomware protection in various ways, from the very simple to the most advanced.
Immutable snapshots provide the most basic level of protection. These allow administrators to revert to a healthy state if data is compromised by ransomware. While foundational for ransomware protection, this feature is reactive and doesn’t provide proactive insights. It’s only after the environment has been hit and the ransomware detected that administrators can use immutable snapshots to recover from the attack.
Combining immutable snapshots with other techniques, such as replication, provides an intermediary level of protection. In this case, snapshot data is replicated to a dedicated, isolated system or to the cloud. Additional capabilities, such as basic detection and snapshot recovery orchestration, may also be included.
The most advanced implementations provide sophisticated ransomware identification algorithms trained using AI/ML models. They’re able to analyze a broad range of patterns and anomalous behaviors and correlate seemingly isolated incidents to identify potentially harmful scenarios. These detection patterns include usual activity times in a given geographic area, data types typically accessed and user access patterns, and large-scale file operations across folders and shares. In addition, advanced solutions implement proactive mitigation strategies, such as the identification of systems and accounts that are the source of these changes, the ability to revoke access of potentially impacted users and systems, and the possibility of cutting off access to parts or all of the affected file systems. Finally, these solutions integrate with monitoring and AIOps platforms, providing comprehensive alerting and active mitigation options.
Ransomware creators implement various techniques to avoid immediate detection. For example, ransomware can make its way into an organization’s environment but stay dormant for weeks or months. It can also perform staggered activities, affecting only a few files at a time, usually those that haven’t been accessed for months or years. However, this focus on old files, unnoticed by humans, is easy for the storage platform to detect.
Finally, some ransomware creators are also implementing partial encryption to evade recognition via indirect observation metrics such as sudden drops in data compression rates combined with steep increases in data change rates. Advanced attacks have been reported that include injecting storage drivers into the operating system layer: data is encrypted in the back end, at the block storage LUN or logical unit number level, but the storage driver decrypts data and transparently provides access to it until the attacker enables a kill switch and completely disables data access.
With the growth of ransomware protection solutions and the increased focus on proactive monitoring, the concept of encrypting old files first in an indiscriminate manner is losing its appeal and may make room for random patterns that are more difficult to identify. On the other hand, AI-based ransomware protection solutions are regularly updated and trained to catch up with new threat models and identify them.
Market Segment
To better understand the market and vendor positioning, we assess how well NAS solutions with integrated ransomware protection are positioned to serve specific market segments (Table 1). Note that we’re looking only at ransomware capabilities offered by primary storage vendors, not at dedicated, standalone ransomware protection solutions.
- SMB: In this category, we assess solutions on their ability to meet the needs of organizations ranging from small businesses to medium-sized companies, including departmental use cases in large enterprises. For these use cases, the solution should provide a turnkey experience and a complete feature set suited to the IT generalist. The solution should compensate for the limited resources of these organizations and the unavailability of dedicated personnel, such as IT specialists or information security experts.
- Large enterprise: Here, offerings are assessed on their ability to support large and business-critical projects. Optimal solutions in this category focus on the feature set depth and integration with existing enterprise tools, such as data protection solutions, information security tools, AIOps, and IT service management (ITSM) platforms. Scalability and flexibility are key to successful enterprise adoption.
Table 1. Market Segment
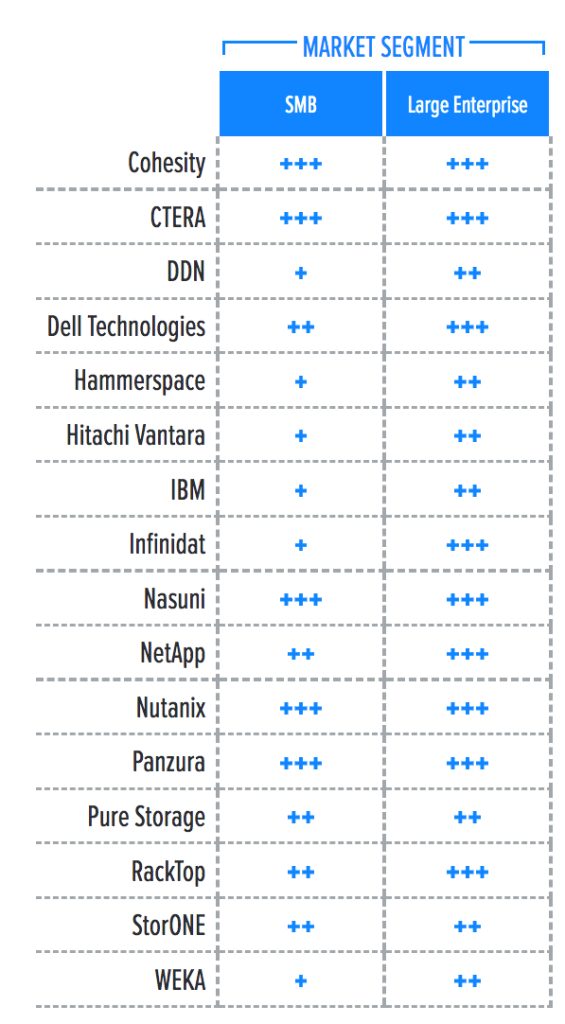
+++ Exceptional: Outstanding focus and execution
++ Capable: Good but with room for improvement
+ Limited: Lacking in execution and use cases
– Not applicable or absent
3. Considerations for Adoption
The purchase drivers for adopting ransomware protection deployed on file-based primary storage are very clear. The only potential downside is that a storage system embedding advanced ransomware protection may be more expensive than a storage system without such capabilities. On the other hand, the benefits are so overwhelming that organizations should seriously consider whether purchasing a storage solution without ransomware protection capabilities makes sense.
Prospective customers should carefully consider the following when evaluating solutions: first, how the primary storage ransomware protection fits within their overall security, threat, and ransomware protection posture; and second, how the solution integrates with their broader threat mitigation strategy.
A primary storage solution that provides only immutable snapshots as a ransomware protection layer would be acceptable for an organization that has invested in advanced, dedicated ransomware protection. However, this would be insufficient for organizations that can’t afford the same investment in a dedicated ransomware solution, or organizations that are refreshing their primary storage arrays and investing in security at the same time.
Similarly, organizations with a heterogeneous storage infrastructure might question the benefits of a deeply integrated and advanced ransomware protection solution that is proprietary to a single storage vendor.
Another consideration is the scope of a given solution compared to the broader infrastructure footprint. If the customer manages other storage types and one vendor’s solution supports both file and block systems, this could be an advantageous choice for the organization.
In any case, determining the current security posture of an organization, where it plans to take that posture next, and the available budget will help further refine the appropriate adoption criteria.
Key Characteristics for Enterprise Adoption
Here we explore the key characteristics that may influence enterprise adoption of the technology based on attributes or capabilities offered by some vendors but not others. These criteria will be the basis on which organizations decide which solutions to adopt for their particular needs.
These key characteristics for primary storage ransomware protection are:
- Architecture
- Enhanced immutability
- Proactive identification
- Mitigation and recovery
- Air gap
- Monitoring and analytics
The design, implementation, and feature set of ransomware protection solutions can impact scalability, performance, and efficiency. Solutions tightly embedded within the storage platform will provide immediate results but will lack the kind of global view that is better able to identify anomalous patterns happening either at scale or in specific locations. On the other hand, other solutions may use a different model based on a centralized AI/ML proactive detection system to which suspicious patterns are sent for analysis and training purposes.
Enhanced Immutability
Even if data immutability is a foundational capability of ransomware protection, simple implementations can be bypassed by malicious actors. Network Time Protocol (NTP) DDoS attacks can be used to trick the system and cause the snapshot retention period to lapse, giving the attacker the ability to delete snapshots that should have been immutable. In addition, the lack of multiple-administrator validation controls can allow an attacker to delete data retention policies and snapshots without any safety checks. Solutions with enhanced immutability features add an extra security layer to protect against tampering, implement enhanced action validation controls, and deliver additional retention mechanisms to allow the recovery of deleted snapshots.
Proactive Identification
Basic ransomware protection features such as snapshots and continuous data protection are now taken for granted. Ransomware infection patterns are nearly imperceptible to IT personnel, who often realize the extent and impact of a ransomware attack only after it’s too late to react. Advanced ransomware protection systems are trained on ransomware behavioral patterns that can identify anomalous behavior by analyzing file system changes in real time.
Mitigation and Recovery
Although timely identification of infection patterns is crucial, alerting is not sufficient. The solution should implement techniques to isolate encrypted data and contain the spread; for example, by terminating active connections to the file system or temporarily restricting access. Similarly, it must implement methods to recover the impacted data easily.
Air Gap
To further protect data, some vendors implement air gapping, a method of securely replicating the data from primary storage to an isolated environment that can be located either on-premises or in the cloud, and is sometimes even provided as a service.
Monitoring and Analytics
Monitoring and alerting capabilities and the ability to visualize threats and their impact are essential. The solution should include a management interface with proactive alerting capabilities, and it should integrate with enterprise system management solutions and security alerting/monitoring tools, AIOps, and ITSM tools.
Table 2 shows how well these key characteristics are implemented in each of the solutions assessed in this report.
Table 2. Key Characteristics Affecting Enterprise Adoption
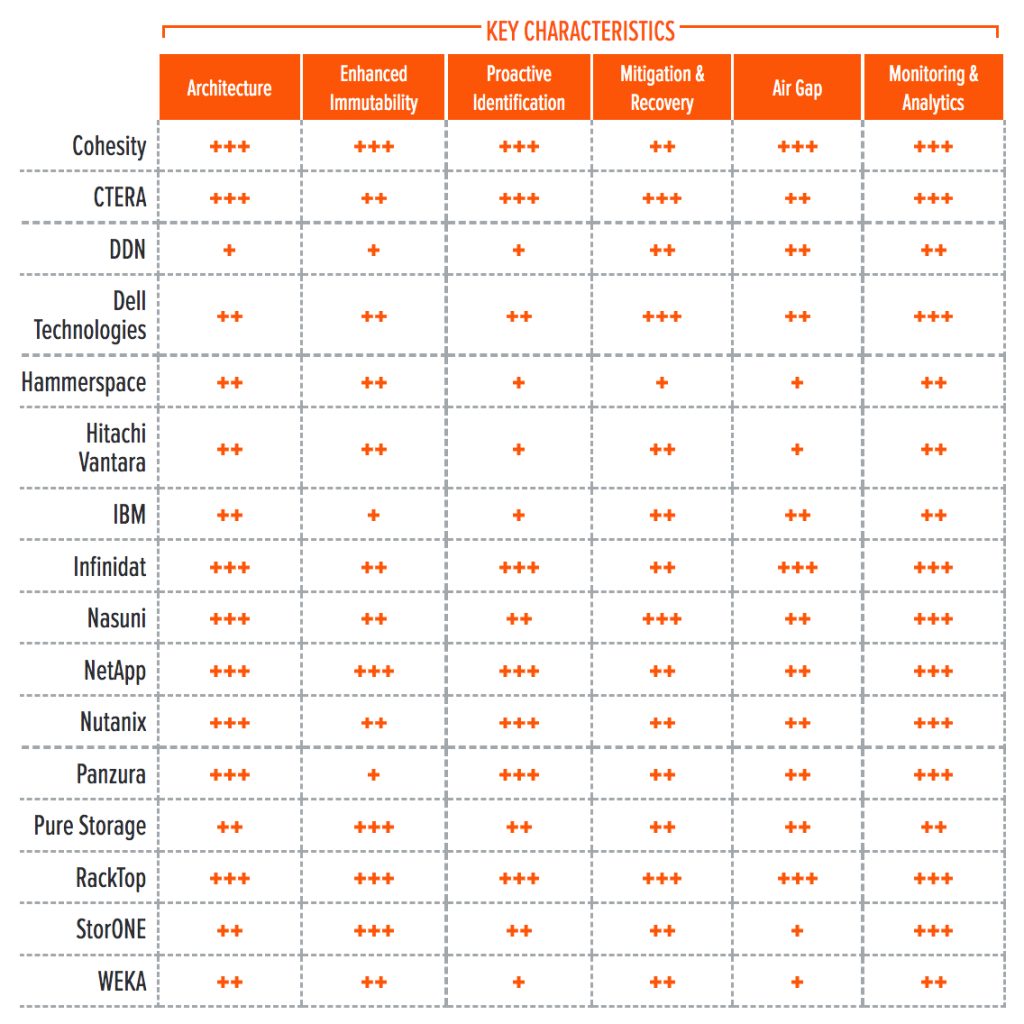 +++ Exceptional: Outstanding focus and execution
+++ Exceptional: Outstanding focus and execution
++ Capable: Good but with room for improvement
+ Limited: Lacking in execution and use cases
– Not applicable or absent
4. GigaOm Sonar
It provides a forward-looking analysis of vendor solutions in a nascent or emerging technology sector. It assesses each vendor on its architecture approach (Innovation), while determining where each solution sits in terms of enabling rapid time to value (Feature Play) versus delivering a complex and robust solution (Platform Play).
The GigaOm Sonar chart (Figure 2) plots the current position of each solution vs. these three criteria across a field of concentric semi-circles, with solutions set closer to the center judged to be of higher overall value. The forward-looking progress of vendors is further depicted by arrows that show the expected direction of movement over a period of 12 to 18 months.
Figure 2. GigaOm Sonar for File-Based Primary Storage Ransomware Protection
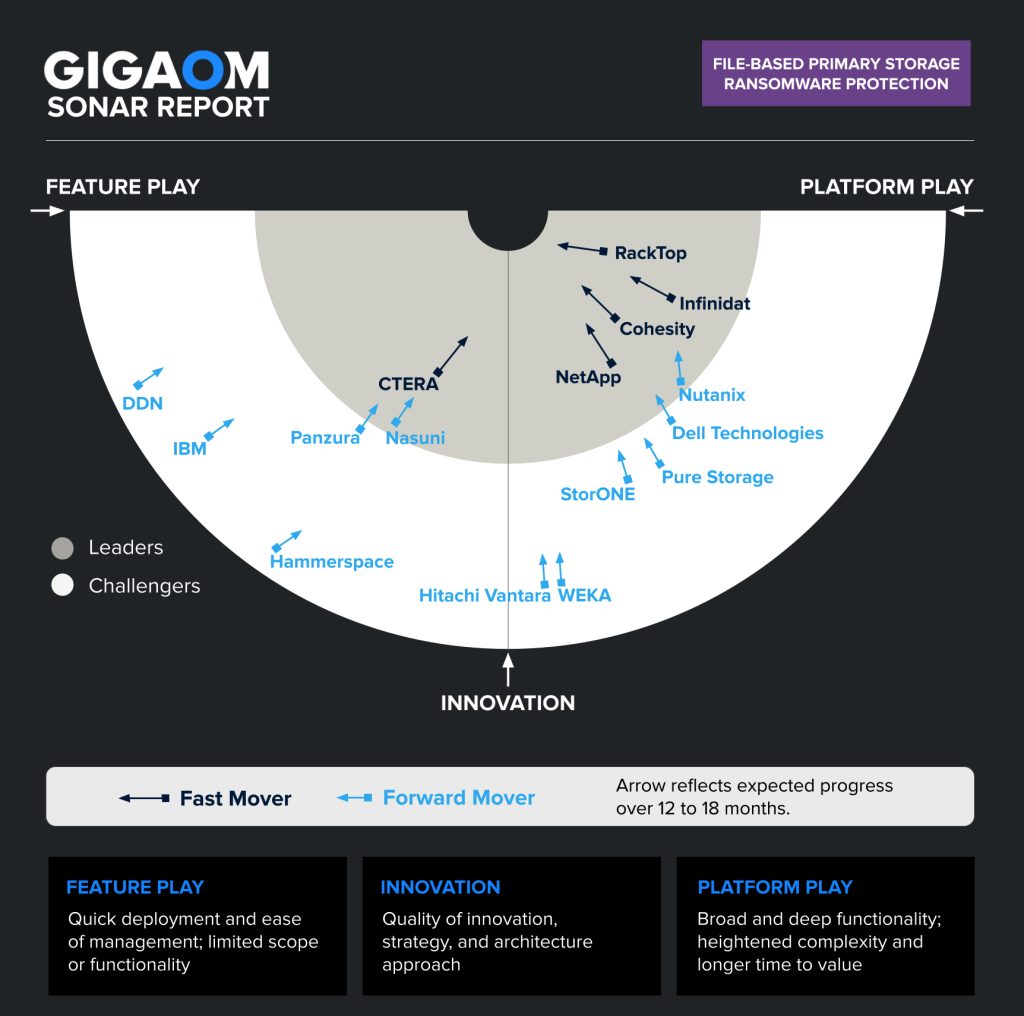
As you can see in the Sonar chart in Figure 2, ransomware protection solutions for file storage are spread across the entire chart; however, several distinct groups can be identified. Note that compared to last year, the Sonar format has changed, along with some of the key characteristics, which introduced some placement changes.
Within the Leaders circle, a large group is shown on the Platform Play side on the right , which is reserved for solutions with broad functionality. This group comprises RackTop, Infinidat, Cohesity, NetApp, and Nutanix.
RackTop’s solution intertwines file storage and data security within its BrickStor SP software-defined solution, embedding a comprehensive set of ransomware protection capabilities delivered through a zero-trust approach.
Infinidat offers a complete and balanced ransomware protection solution with InfiniGuard CyberRecovery, which has been enhanced this year with InfiniSafe Cyber Detection, an ML-based, petabyte-class proactive ransomware detection solution.
Cohesity continues to deliver on the cyber resiliency promise with proactive ML-based detection, on-premises and cloud-based immutability capabilities, and strong zero-trust and anti-tampering features, augmented with data protection and data management features inherent in the platform.
NetApp delivers a strong set of ransomware protection capabilities at multiple layers, while also working on rationalizing and better integrating its portfolio of cyber resiliency features.
Nutanix Data Lens offers a commendable SaaS-based data security solution for ransomware resilience and global data visibility with features such as proactive threat containment and alerting capabilities.
The second group of Leaders is found on the left, Feature Play side of the chart, and consists of CTERA and Nasuni. Although the scope of these solutions is narrow, they are well integrated and offer a fast time to value.
CTERA recently released Ransom Protect, a homegrown AI-based proactive ransomware detection solution that completes the company’s cyber resiliency feature set.
Nasuni’s ransomware protection includes fast recovery, mitigation with plans for automated recovery orchestration, and a proactive ransomware detection solution that is being actively improved.
Notice that Panzura, currently in the Challengers’ band, is shown crossing toward the Leaders band. The solution offers a good balance between proactive detection, mitigation, and recovery capabilities on one hand and peripheral insights that can also help, although automated recovery orchestration needs to be developed.
The next group consists of Challengers on the Platform Play side.
Dell Technologies has built comprehensive ransomware protection capabilities for its PowerMax storage platform, available with both block and file volumes. For its PowerScale offering, the company relies on integration with Ransomware Defender, a separately licensed solution developed by Superna, a company in which Dell invests.
Pure Storage provides ransomware protection through its SafeMode snapshots (now enabled by default) and strong multifactor authentication (MFA), and has added security posture features to its solution. It also delivers a ransomware recovery SLA, an add-on service that helps customers recover faster in case of attack.
StorONE offers a well-balanced solution and improves the ransomware protection capabilities with a proactive detection feature called anonymous detection.
WEKA currently offers basic ransomware protection with Snap-To-Object, a feature that enables immutable snapshots to be stored locally and in object storage, and WEKA Home, cloud-based anomaly detection that doesn’t yet support monitoring of third-party storage repositories.
Hitachi Vantara licenses WEKA’s solution and thus has the same characteristics and positioning, although the company has no control over the product roadmap.
The remaining vendors are Challengers on the Feature Play side. These solutions focus on specific use cases, which means their scope or feature set may be limited.
Among these, Hammerspace offers a very good immutability feature set which can be combined with automatic versioning and data orchestration automation for recovery, but proactive ransomware detection capabilities are currently missing.
DDN also offers immutable snapshots and cloud-based monitoring but it has no proactive ransomware detection capabilities and relies instead on indirect evidence via monitoring of ransomware-related metrics.
Finally, IBM’s Storage Scale (previously known as Spectrum Scale) parallel file system, although not initially designed to handle general-purpose file workloads or combat ransomware, offers granular control over immutability settings, improved retention settings, and indirect monitoring of ransomware-related I/O metrics.
Note that Datacore was removed from this year’s report as the company has discontinued vFilO, its offering based on Hammerspace technology, and currently does not offer a replacement solution.
5. Vendor Insights
Cohesity
It offers a compelling solution that meets data protection, cyber resiliency, and data management challenges in hybrid cloud scenarios with its Cohesity Cloud Data Platform. It offers sophisticated data protection via SmartFiles, a software-defined file and object service that runs on the platform that provides ML-based early detection of attacks by monitoring data changes against normal patterns and measuring abnormal activity against the usual activity baseline. In addition, its user behavior analytics (UBA) make it easy to detect risky user behaviors and indicators of data exfiltration, tampering, deletion, and more. It also audits user file activities with interactive log search.
Cohesity also supports immutable snapshots and protects against attempts to modify them, a capability at the core of its SpanFS file system. The solution implements rapid recovery that leverages fully hydrated copies, local search, ML-based recommendations, and patented technologies to recover volumes, objects, databases, and VMs to any snapshot point in time, and to reinstate instant NAS access. To further strengthen immutability, the company offers FortKnox, a strongly secured, isolated cloud air-gap immutable storage solution that is delivered as a service.
The solution provides additional protection measures and anti-tampering techniques, like preventing network time protocol (NTP) attacks. These attacks usually trick the servers and data protection systems into moving time forward to artificially expire immutability flags on locked datasets. Cohesity protects against such attacks by never moving the time forward more than 10 minutes per 14-day period, even if time servers ask to jump forward.
Another differentiator is a strong zero-trust MFA module with quorum-based approval for sensitive actions in the environment, such as changing protection policies. Organizations can define which individuals can approve sensitive actions. Then, any authorized individual launching a sensitive action will trigger an approval workflow requiring a quorum before the action goes into effect. The quorum-based approval feature offers full granularity and permits the creation of multiple groups, each covering specific options, allowing full customization based on an organization’s internal policy and security posture.
This approach is further enhanced by Cohesity DataHawk (formerly DataGovern), an add-on that provides automated threat intelligence by simplifying threat detection using a deep learning-based engine. DataHawk integrates a set of highly curated and managed indicators of compromise (IoC) threat feeds that are updated daily and extensible to third-party integrations via security information and event management (SIEM) or security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) solutions. DataHawk also addresses compliance requirements by providing quick and simple access to finding, identifying, and classifying regulated data such as PII, HIPAA, and PCI, and it includes over 200 classifiers and more than 50 predefined policies with ML-based pattern matching and recognition. DataHawk quickly scans and automatically classifies data from VMs and file shares, simplifying security and compliance.
These capabilities are easy to manage and are provided through a single management pane. The features can also be used in the context of data protection components present in the Cohesity platform.
Strengths: Offers a very strong cyber-resiliency approach that includes proactive ML-based detection, on-premises and cloud-based immutability capabilities, and strong zero-trust and anti-tampering features. The platform approach allows to thrive not only with file-based ransomware protection but also with data protection and now data management with DataHawk.
Challenges: Although the company offers full-featured ransomware protection via its SmartFiles solution, the Cohesity Data Platform is usually not deployed as a file-based primary storage solution.
CTERA
It presents a distributed cloud file storage platform built around its Global File System (GFS), which can reside in the cloud as well as in on-premises infrastructure. Organizations can access GFS through three components: a CTERA Edge Filer gateway (a server message block/SMB and network file system/NFS network filer, which can be deployed centrally or at edge locations with a compact HC100 Edge Filer), the CTERA Drive (a desktop/VDI agent), or the CTERA mobile application.
The solution implements read-only immutable snapshots and continuously replicates those snapshots to the cloud on immutable object storage. Using CTERA’s ‘instant disaster recovery’ feature, the snapshots can be instantly recovered from the cloud so that users can immediately access the data as it is being recovered in the background. If a file that was not yet recovered is accessed, it is pulled from the cloud in real time, prioritizing actively used files first.
Additionally, the solution implements WORM folders feature. With WORM folders, users can designate specific folders as fully immutable, going beyond the scope of immutable snapshots. Data stored in these folders cannot be altered or deleted, even by malicious actors or ransomware attacks. Administrators can set compliance policies on WORM folders to ensure data integrity and regulatory adherence.
For the most security-sensitive organizations, CTERA also supports AWS cross-account bucket replication to air-gap data in case administrative credentials are compromised. Other features include a zero-trust architecture that prevents exploitation of edge filers to access central data, and MFA for administrator access and validation of certain sensitive operations, such as permanent content deletion.
Proactive detection is handled by CTERA Ransom Protect, a feature released at the beginning of H2-2023. CTERA Ransom Protect is an integrated, homegrown AI-based ransomware detection and prevention system that runs on CTERA Edge Filers. It detects ransomware within 30 seconds based on behavioral analysis, blocks the offending users, and sends relevant warnings with audit trail information. This feature allows administrators to monitor attacks in real-time through dashboards and provides near-instant recovery when customers use CTERA’s instant disaster recovery feature. CTERA Ransom Protect relies on real-time AI detection and advanced ML algorithms to identify behavioral anomalies instead of relying on traditional signature update services. Its ML algorithm does not require an initial training phase.
Third-party integration with Varonis is still supported and allows organizations to monitor and analyze logs, assist with data classification, and identify risky permission settings. A single instance of Varonis is required for an entire organization using CTERA, mitigating the added complexity of working with a third-party vendor. An integrated antivirus feature performs virus scanning both on edge filers and in the cloud. Finally, organizations can send CTERA logs to their SIEM platform through syslog forwarding.
CTERA’s immutable snapshots, the built-in ransomware protection, and antivirus capabilities are part of the solution’s feature set and do not incur extra licensing fees. Varonis integration works under a BYOL (bring your own license) model.
Strengths: With the release of Ransom Protect, now has comprehensive coverage of ransomware protection, offering immutability, mitigation and remediation, and proactive capabilities.
Challenges: Ransom Protect was launched very recently and is not yet proven in the field.
DDN
Its IntelliFlash platform delivers unified file and block storage and includes features that protect against ransomware attacks: IntelliCare Cloud Analytics for detection and IntelliFlash immutable snapshots for remediation. Although the solution provides a strong foundation with immutable snapshots, these are now considered table stakes, and the company hasn’t introduced to its solution any advanced immutability capabilities, such as enhanced control over snapshot policies, multiple-administrator validation, or soft-delete of immutable snapshots past their retention period.
For monitoring and analytics, IntelliFlash leverages IntelliCare Cloud Analytics to identify unusual storage growth and generate alerts. The solution is capable of identifying anomalies but does not provide any direct observation, nor does it offer any proactive response such as terminating connections or quarantining users or file shares.
If a ransomware attack is confirmed, IntelliFlash snapshots can be used to rapidly revert to a prior healthy state. Snapshots can be scheduled and enabled from IntelliFlash’s management interface with the ability to land snapshots on-premises, in the cloud, or both, and to store data at multiple locations. There is, however, no recovery orchestration capability available. Similarly, with regard to air gapping, the solution allows manual configuration of a secondary system with snapshot scheduling, but there is currently no reference architecture or dedicated air gap offering that would allow customers to quickly implement air gapping for recovery from a ransomware attack.
Although not evaluated as part of this report, Tintri (a company owned by DDN) implements advanced ransomware capabilities on its Tintri VMStore storage appliances. Tintri VMStore provides ML-based ransomware protection capabilities; however, VMStore is targeted only at virtualized workloads and provides a storage abstraction similar to VMware vVols, so it does not fit into GigaOm’s classification of block or file storage.
Strengths: Provides a basic set of ransomware protection features on its IntelliFlash platform, including basic monitoring capabilities and immutable snapshots.
Challenges: Detection capabilities are limited and indirect. The solution has no recovery orchestration and no dedicated air gap offering.
Dell Technologies
It delivers ransomware protection through a combination of storage array capabilities, CloudIQ, and integration with 3rd-party software that specializes in ransomware protection and other security functions. Four primary storage solutions offer file storage capabilities: PowerScale, Dell’s scale-out file system based on OneFS, and three unified block and file storage arrays: the PowerMax, PowerStore, and PowerFlex appliances.
PowerScale’s native snapshot functionality provides read-only snapshots that can be anchored at the filesystem, share, folder, subfolder, or individual file level. OneFS role-based access control (RBAC) can separate the ability to create and delete snapshots according to user types, and the delete snapshot capability can be removed for all users except the root account if desired. OneFS’ native change-tracking functionality also allows an administrator to identify any altered files by comparing the active file system to a snapshot, or a snapshot to other snapshots. The snapshots can also be replicated to separate PowerScale units or to S3-based object stores. Dell also offers a smart air gap capability, and the PowerScale OneFS operating system includes a comprehensive set of built-in enterprise-grade security features, including WORM SmartLock compliance.
The companys relies on Superna’s Ransomware Defender, a software suite developed specifically for PowerScale and ECS that runs externally to the storage array to provide real-time ransomware detection, response, and mitigation activities. Ransomware Defender is scalable to multiple arrays and sites. It proactively monitors the PowerScale and ECS platforms for threats and can trigger automated response scenarios such as locking users out, taking snapshots, suspending schedule replication or copy jobs, and more. Ransomware Defender can also identify files impacted by a ransomware attack and offer targeted data recovery, making recovery faster and more efficient. Threat responses will be orchestrated among all systems at all sites that are monitored by Ransomware Defender.
Ransomware Defender has other security and protection functions, such as live wiretap generation for inspection of client real-time activity. It can also simulate penetration tests and execute scheduled failover tests for any replication sessions for PowerScale. Optional plug-ins for Ransomware Defender include a geo-fencing feature, a zero-trust API, data target integration with network appliances and devices, and an isolated vaulting function.
PowerMax, PowerStore, and PowerFlex file services are provided by a common engine known as SDNAS. On the PowerMax platform, proactive ransomware protection capabilities can be delivered through CloudIQ. PowerMax provides telemetry data in near real time to CloudIQ, which monitors and detects anomalies in the observed client behavior, assesses adherence to security baselines, and identifies incidents such as potential ransomware attacks. Alerts are generated and pushed to administrators through various methods and can be integrated with ITSM and SIEM platforms to automatically create incidents and initiate investigation activities.
All SDNAS snapshots are natively immutable (read-only), and all SDNAS systems, along with PowerScale OneFS, support the Common Event Publishing Agent (CEPA) service, which allows integration with 3rd-party solutions that specialize in ransomware defense and detection, such as Netwrix StealthDEFEND or Varonis DatAdvantage.
Although out of scope for this report, the firm also offers ransomware protection for all of the firm’s storage platforms via Dell PowerProtect Cyber Recovery, which also delivers air gap capabilities.
Strengths: For file storage, offers a balanced set of ransomware protection capabilities in its PowerScale platform, combining proactive detection and immutable snapshots with additional recovery orchestration capabilities on PowerScale.
Challenges: Offers two very distinct approaches to ransomware protection: consolidation of capabilities via CloudIQ or the integration of Superna technology. This could be an opportunity for the company to simplify ransomware protection operations in environments where various Dell Technologies storage platforms coexist.
Hammerspace
Its parallel global file system helps overcome the siloed nature of hybrid multivendor, multiple-data center, and cloud file storage by providing a single file system regardless of a site’s geographic location or whether storage provided by any storage vendor is on-premises or cloud-based. It also separates the control plane (metadata) from the data plane (where data actually resides). The solution is compliant with several versions of the NFS and SMB protocols and includes RDMA support for NFSv4.2.
The company lets customers automate via objective-based policies that allow them to use, access, store, protect, and move data around the world through a single global namespace, so users don’t need to know where the resources are physically located. The product is based on the intelligent use of metadata across file system standards and includes telemetry data (such as IO/s, throughput, and latency) as well as user-defined and analytics-harvested metadata, allowing users or integrated applications to rapidly view, filter, and search the metadata in place instead of relying on file names.
Firm’s ransomware protection strategy relies on native immutability features, monitoring, and third-party detection capabilities. The vendor also offers global monitoring through file telemetry, which is part of the objectives-based policy engine. While not designed in the current product to explicitly detect ransomware attacks, it nevertheless provides real-time feedback to administrators when files and file volumes are out of alignment with defined objectives, or impacted by unexpected disruptions.
Customers can take advantage of firm’s automated antivirus scanning directly or through a third-party integration with their own antivirus solution (via the iCAP protocol). Hammerspace implements floating IP addresses for its nodes, obfuscating the back-end infrastructure and making it more difficult for an attacker to discover on which nodes data is stored. The company can provide global reach across all silos, even multisite and cloud, giving third-party anomaly detection solutions unprecedented reach.
On the remediation side, it implements immutable file shares with global snapshot capabilities, both on-premises and in the cloud. Snapshots can also be restored to a different Hammerspace system if the source system is compromised. Two other mitigation functions are undelete and file versioning, allowing users to revert to a file version not affected by ransomware-related data corruption. Firm’s ability to automate data orchestration for recovery is a core part of the Hammerspace feature set: global snapshots can be taken across all underlying storage silos, including object, cloud, an so on, and may be stored in one or more instances anywhere, facilitating data recovery in case of an attack.
Immutability functions and built-in antivirus scanning are part of the solution’s basic feature set and do not require additional licensing.
Strengths: The solution sports a good set of mitigation and recovery features with immutable snapshots on-premises and in the cloud, flexible restores, and undelete and file versioning functions.
Challenges: Besides native immutability features, ransomware protection capabilities are limited and require third-party integrations.
Hitachi Vantara
It offers file storage capabilities through the WEKA Data Platform, a SDS solution based on WEKA technology. The feature set is similar to that offered by WEKA, except for the branding and management interface. Customers with a strong Hitachi Vantara footprint may want to choose the Hitachi Vantara flavor of the WEKA technology for licensing and integration purposes.
The WEKA Data Platform is a massively scalable single data platform that provides mixed workload capabilities and multiprotocol support (SMB, NFS, S3, POSIX, GPU Direct, and Kubernetes CSI). It is often used in demanding environments that require low latency, high performance, and cloud scalability.
WEKA supplies a proactive cloud-based monitoring service called WEKA Home that collects telemetry data (events and statistics) and provides proactive support in case of detected warnings and alerts. It can also detect encryption within the underlying storage devices in each storage host by detecting alteration of the block checksum. The solution also supports log forwarding to inhibit tampering by a malicious actor or a rogue administrator.
The multiprotocol nature of the WEKA solution and its ability to run natively in the cloud enable it to use snapshots as mitigation against ransomware attacks. This mitigation capability is delivered through its Snap-to-Object feature, which allows data snapshots to be stored in object storage, either on local or cloud object repositories. With Snap-to-Object, data can be protected with immutable object-based snapshots that help safeguard data against ransomware attacks.
WEKA Home can monitor events and alerts across all WEKA Data Platform deployments; however, the solution can’t be used to monitor third-party storage repositories. From a licensing perspective, Snap-to-Object is part of the base capabilities of the WEKA solution, and WEKA Home is provided free of charge to Hitachi customers with a valid support contract.
Strengths: Thanks to its partnership with WEKA, Hitachi offers a straightforward solution that combines monitoring and detection capabilities with immutable object storage, snapshots, and the flexibility of using local or cloud-based repositories.
Challenges: From an ecosystem standpoint, the solution is limited only to WEKA deployments, and in terms of development, Hitachi is dependent on the WEKA Data Platform’s roadmap.
IBM
It supports ransomware protection capabilities on its Storage Scale parallel file system with an immutable filesets feature, which implements immutability at the file level, providing append-only capabilities that are available via both SMB and NFS protocols.
The immutability of files is controlled through file-system-level attributes configured either through Storage Scale’s Integrated Archive Manager (IAM) or standard POSIX commands. Storage Scale immutability supports multiple IAM modes that allow granular control of immutability attributes on a given fileset. The solution’s capabilities are very similar to the NetApp SnapLock feature, as cited in IBM Storage Scale documentation. (IAM even implements a SnapLock-compatible IAM mode).
In version 5.1.5 of Storage Scale, Big Blue introduced a snapshot retention mechanism that prevents snapshot deletion at the global and fileset level, effectively bringing immutability, and thus basic ransomware protection capabilities, to the platform. The expiration time flag requires file systems to be upgraded to version 5.1.5 or later to function. In addition, Storage Scale also works with IBM Safeguarded Copy technology, a solution that uses Storage Scale immutable snapshots to orchestrate data protection and recovery against ransomware attacks.
Early warning signs of an attack can be provided by IBM Storage Insights or IBM Spectrum Control. Both solutions can analyze current I/O workload against a previous usage baseline and help provide indications that an attack is in progress. Organizations can set up alerts that indicate an attack may be happening by combining multiple triggers. For example, a sudden drop in data reduction efficiency could indicate vast amounts of data getting encrypted, rendering de-dupe and compression ineffective. The company also recommends monitoring the write change rate for deviations and anomalies, as well as further integration with a SIEM platform (such as IBM QRadar) for better visibility.
There are currently no particular orchestration or proactive snapshot capabilities.
Strengths: Although not initially designed to combat ransomware, Storage Scale offers granular control over immutability features with multiple immutability modes. The inclusion of a snapshot retention mechanism is a welcome addition that adds foundational capabilities to Storage Scale.
Challenges: The solution lacks proactive detection capabilities. There is room for improvement in terms of manageability and integration between the various building blocks.
Infinidat
It boasts a modern, AI-based hybrid SDS architecture that delivers a no-compromise feature set with compelling $/GB and $/IO/s ratios. To achieve this, its InfiniBox and InfiniBox SSA II storage systems take advantage of a data path designed around a combination of DRAM, flash memory, and HDDs associated with sophisticated AI-based caching technology to optimize data placement. Firm’s core InfiniSafe technology is built into InfuzeOS and is provided at no additional charge.
Ransomware protection is delivered across company’s portfolio through its InfiniSafe technology solution. This solution offers modern data protection, backup, DR, and BC features. InfiniGuard offers backup and recovery performance at scale, covering all data protection needs and easily integrated with leading data protection solutions. As with Infinibox and Infinibox SSA II primary storage platforms, Infiniguard’s ransomware protection capabilities are also enabled by InfiniSafe.
Branded InfiniSafe, the technology provides immutable snapshot copies of source data sets that incorporate logical air-gapping—both local and remote. When a customer undergoes a cyberattack, they can move the copies into a secure fenced network to check for malware or ransomware. Known good copies of the data are identified, and the customer can make a near-instantaneous guaranteed recovery of the known good copy in less than a minute for petabyte-scale primary datasets on the InfiniBox and InfiniBox SSA and less than 20 minutes for backup datasets on the InfiniGuard. InfiniSafe Cyber Storage guarantee is provided on InfiniBox, InfiniBox SSA, and InfiniGuard platforms.
The company recently introduced InfiniSafe Cyber Detection, an ML-based, petabyte-class solution built on vendor’s indexing capabilities, which targets primary storage (volumes, snapshots), databases (like Oracle, DB2, SQL, and SAP HANA), and user files. This solution uses 200 points of determination with 99.5% accuracy to identify highly granular attacks, including partial encryption. It organizes alerts by severity, provides relevant details, and generates forensic reports. It also makes corrupted files available for download for further analysis and will tag corrupted files. The solution runs on a separate server (or more) and scans attached snapshots and volumes. It can also scan on a secondary source; data can be replicated to a target system, then scanned there. As of launch time, the solution supports block and file workloads and will support backups later in 2023.
Strengths: InfiniSafe delivers a fully fledged set of cybersecurity features at no extra cost, allowing customers to quickly and securely restore data, even at scale, in case of an attack. The addition of proactive detection is a major milestone for Infinidat.
Challenges: InfiniSafe Cyber Detection was recently launched and has not yet been proven in the field.
Nasuni
It offers a SaaS solution for enterprise file services, with an object-based global file system as its main engine and many familiar file interfaces, including SMB and NFS. The solution is integrated with all major cloud providers and works with on-premises S3-compatible object stores. Many firm’s customers implement the solution to replace traditional NAS systems. Its characteristics let users replace a number of infrastructure components, such as backup, archiving platforms, and more.
Nasuni Ransomware Protection is an add-on service that is designed to proactively defend file shares, stop attacks, and give detailed information on files affected by an attack so organizations are able to rapidly return to productivity when an attack occurs. Combined with the Nasuni File Data platform’s core protection and patented rapid recovery capabilities, it delivers enhanced ransomware resilience for file shares regardless of amount of data or where it is located. The service analyzes malicious extensions, ransom notes, and suspicious incoming files based on signature definitions that are pushed to Nasuni Edge Appliances. After an attack is detected, Nasuni mitigation policies will automatically stop the attack in seconds by blocking the client, quarantining the threat, and preventing it from spreading. The vendor implements quorum-based approval for volume deletion, a safe delete feature.
Currently, the solution provides up-to-date intelligence on the latest ransomware variants and can report on all impacted files, impacted users, and source IP addresses. Notifications are provided in the Nasuni UI and via email. They can also be forwarded via syslog to external monitoring platforms for further analysis by enterprise-wide security event monitoring solutions used by security operations center (SOC) experts.
The solution offers integrations with Varonis and Microsoft Sentinel for better protections and insights. The integrations are actively being updated and upgraded to give customers a more secure and ransomware-protected environment. More solution integrations will be implemented as well, as even deeper integrations with the already existing solutions are on the Nasuni roadmap.
On the remediation side, Nasuni Rapid Ransomware Recovery acts as a last line of defense, allowing the recovery of millions of files from within seconds before the attack occurred, with RPO granularity that can go as low as 1mn. The feature takes advantage of firm’s continuous file versioning, a built-in capability that protects data as immutable objects with a near-infinite number of recovery points.
Targeted restore is a new addition to the Nasuni Ransomware Protection solution and provides a streamlined restore process for faster overall recovery and reduced administration time. When an admin moves to the recovery process to set up a restore job, key details, including the affected files and the last clean snapshot before an incident, are automatically identified and queued up. The system will then restore only those exact files to the identified snapshot.
The solution is easy to activate and manage and offers comprehensive protection across the entire customer’s Nasuni footprint. Combined with built-in capabilities such as continuous file versioning, Ransomware Protection can drastically reduce recovery times from more than 12h to less than 1h. As mentioned, it is an add-on paid feature.
Strengths: Offers a complete feature set that covers detection and remediation, provided as an easy-to-deploy add-on service.
Challenges: The Ransomware Protection solution is still in development; key features like ML-based detection capabilities require attention as global training models are currently absent but planned to be released by 4Q23.
NetApp
It offers a ransomware protection portfolio for both on-premises and cloud workloads, with multiple layers of protection. It provides autonomous ransomware protection (ARP), an embedded anti-ransomware capability for primary storage on the ONTAP operating system and its various deployment models. This feature performs workload analysis on SMB and NFS environments and proactively detects and warns about anomalous activities that could be related to ransomware attacks. The solution includes ML capabilities and can identify whether data is encrypted or plain text. It also has an analytics engine that can determine whether the data content of a file matches its extension type, whether there is a surge in volume activities related to data encryption, and whether the file presents specific characteristics, such as high data entropy. The ARP feature is configurable per volume and allows the system to take additional snapshots on top of already existing or scheduled snapshots if abnormal activity is detected.
NetApp Cloud Insights provides additional monitoring capabilities through its Storage Workload Security feature which monitors not only file activity, but analyzes it in the context of the baseline behavior of the user account performing the action across all ONTAP-based storage. It can detect potential accounts, report their discovery, and take certain automated actions such as shutting off access from the suspect account(s) and triggering a preventative snapshot. Full file forensics of that user’s file access and activity for the prior thirteen months are also made available. These protections are incremental to that offered by ONTAP’s ARP feature. The vendor offers multiple-administrator verification for sensitive operations. This can prevent one person from making unauthorized changes to snapshot and replication policies, immutability settings, snapshot deletion, and more.
The NetApp on-box anti-ransomware capability can be combined with other ONTAP features such as FPolicy Native Mode to block known malware extensions, snapshot copies, and SnapLock, and NetApp Active IQ Digital Advisor can provide an additional layer of mitigation and prevention.
These capabilities can be extended through the use of complementary cloud-based solutions from NetApp (such as FPolicy on Cloud Volumes ONTAP), which provide various detection and remediation capabilities, such as those noted earlier with Cloud Insights Storage Workload Security, combined with immutable storage, like cloud WORM. Most of the ransomware capabilities can be handled easily through Cloud Insights and ONTAP System Manager. Cloud Insights also monitors user behavior to detect events not normally considered ransomware, such as multiple insider threats.
FPolicy can be configured in external mode, which collects and supplies information on user actions to an external FPolicy Server in NetApp Cloud Insights; it’s that information which the AI/ML of Storage Workload Security uses to detect user behavior anomalies. Attacks can then be detected and stopped, and the system will send alerts and take snapshot backups, and can optionally block compromised accounts.
The company recently announced a “ransomware recovery guarantee,” which is initially available with NetApp AFF C-Series and ASA A-Series storage purchases. Through this mechanism (which requires NetApp Professional Services and subscription to a NetApp Ransomware Protection and Recovery Service), the firm warrants snapshot data recovery either on primary or secondary ONTAP storage and offers compensation if data can’t be recovered.
Strengths: Offers a fully fledged anti-ransomware implementation and provides both proactive identification and mitigation capabilities, all backed by a local ML engine and Active IQ, which can also provide ransomware mitigation recommendations.
Challenges: Ransomware protection capabilities are still handled through different layers, which NetApp should be consolidated to further integrate and simplify management effort.
Nutanix
It provides a comprehensive platform with varied storage capabilities beyond its initial HCI scope. Its Nutanix Unified Storage (NUS) suite delivers native file, block, and object capabilities. In the context of primary file storage, the solution delivers these capabilities through the Nutanix Files service.
It implements file-based ransomware protection and mitigation capabilities via integrated data security and analytics features, along with Data Lens, an enterprise-grade, SaaS-based ransomware resilience platform that offers an anomaly-detection engine that monitors data activities such as mass file deletions or permission changes. Administrators can define policies and alerts to get informed of potential threats, and Nutanix Files deployments can be monitored globally across clusters. Furthermore, Data Lens can baseline normalized cluster behavior across thousands of deployments, providing better anomaly detection capabilities. It comes with known and unknown signature based ransomware detection and blocks suspicious files and users in the case of a potential attack. Threat mitigation is simplified with over 5,800 up to date ransomware signatures embedded today.
Nutanix Files provides immutable snapshots and WORM policies, which prevents tampering and deletion. Those native snapshots make recovery easy, and organizations can also take advantage of a secondary level of immutable storage with Nutanix Objects, which delivers immutable object storage and support for WORM policies.
By default, the company implements hardening features that can be used to prevent ransomware attacks. Adherence to security baselines and monitoring against baseline deviations are handled through Nutanix Security Central, a security monitoring and management platform that works across multiple Nutanix deployments. The solution also has strong support for compliance, with several standards supported (FIPS, DoDIN APL, and so forth), and embeds a fully fledged security technical information guides (STIG) compliance setup.
Strengths: Delivers a strong value proposition with proactive ransomware detection and alerting capabilities, security hardening features, and instant data recovery through immutable native snapshots.
Challenges: Recovery orchestration mechanisms are currently limited, but the firm plans to improve them in the near-term roadmap.
Panzura
It offers a distributed file storage solution based on its CloudFS file system. This solution works across public and private clouds and provides a single data plane with local file operation performance, automated file locking, and immediate global data consistency. It also supports a broad range of on-premises and cloud-based object storage solutions.
Proactive threat identification is handled through Panzura Data Services. The solution implements various anomaly-detection mechanisms that are used for ransomware detection and protection. When a suspicious activity that follows ransomware patterns is detected, Data Services can identify, alert, and shut down access to data repositories to prevent further damage.
Ransomware mitigation is handled with a combination of immutable data (using a WORM S3 backend), with read-only snapshots taken every 60s at the global filer level, regularly moving data to the immutable object store and allowing seamless data recovery in case of a ransomware attack. The recovery mechanism is significantly faster than a backup-based recovery, with better granularity and resource use, and it incurs no storage penalty.
Data Services provides comprehensive auditable information for data stored on CloudFS regarding user activities such as data copy, file and folder creation, file system operations, and changes in attributes and permissions. This information is accessible and can be filtered to refine by audit action and date range or user; the solution can return millions of results in under a second. Data Services can be used to identify impacted files or users and actions that may have impacted files and/or permission sets, helping to narrow the scope of an attack’s potential impact and reach. In addition, Panzura’s global services team also helps customers to recover from an attack.
The solution is easy to manage via firm’s management console. Ransomware mitigation capabilities are baked into the solution and provided at no extra cost. However, enhanced ransomware protection, which handles proactive threat identification, is subscription-based.
Strengths: Implements a solid set of ransomware identification, protection, and recovery mechanisms, with additional peripheral insights that can be useful in identifying and combating vectors for ransomware attacks.
Challenges: There is no automated recovery orchestration mechanism yet, though this will soon be included.
Pure Storage
It offers multiple storage products. Among them, FlashBlade delivers unified fast file and object storage capabilities, while FlashArray focuses on block and file storage.
To protect vs. ransomware attacks, it implements immutable snapshots in both solutions. Snapshots can be turned on for blocks and files on FlashArray and for files on Flashblade. However, while the data in the snapshots is immutable, the snapshots could be deleted by an attacker with rogue administrative access.
A feature called SafeMode, built into both storage array types, locks snapshots and prevents their deletion. On FlashBlade, SafeMode snapshots can be used to create a read-only protected snapshot of a full backup, including the backup and associated metadata catalogs as well.
Instead of the standard deletion process, entities such as volumes or snapshots are destroyed and moved into a staging “destroyed” area for a predefined period of at least 24 hours and up to 30 days, with the company recommending at least 14 days of retention. This incompressible timeframe locks any entity in the “destroyed” area and prevents it from being wiped until the timer has expired.
SafeMode is built into the storage solution’s operating system and enabled by default. Recently the vendor introduced Enhanced SafeMode Management, which is a more streamlined multiple-party authentication process compared to the previous solution.
To further improve ransomware recovery, it recently introduced a ransomware recovery SLA for its EverGreen//One offering. This add-on service guarantees a clean storage environment will be shipped the next business day after a customer has been hit by a ransomware attack, and includes a joint design service between the company and the customer at sign-up time to plan recovery steps in case of an attack. The ransomware recovery SLA also guarantees recovery of operations within 48 hours at a transfer rate of 8TB/hour. Finally, the organization can keep this loaned storage array for up to 90 days in order to fully restore operations past the initial 48-hour recovery window.
SafeMode snapshots are configured through Pure1, vendor’s management, analytics, and support platform. Pure1 can also assess whether SafeMode snapshots are enabled across all company’s storage arrays.
Te firm added a data protection assessment feature to Pure1 to ensure the FlashBlade and FlashArray systems follow company’s recommended security practices. This feature analyzes the entire vendor’s estate and determines whether SafeMode is fully or partially enabled on each array and verifies snapshot expiration policies and other factors such as adherence to security guidelines. These take into account local snapshot policies as well as remote policies and whether snapshots are replicated or not. Finally, this feature provides guidance on improving the security posture with actionable insights.
Although the company doesn’t provide a proactive ransomware detection solution, it does provide anomaly detection capabilities, available in the Pure1 data protection dashboard. Pure1 monitors the data reduction ratio of storage appliances, a metric that combines the level of de-dupe and compression that firm’s arrays typically offer to a customer. In case of sharp, anomalous drops (for example, large-scale encryption and/or data deletion), the system will generate alerts to inform administrators about potential malicious activity so they can take further action. Those capabilities are expected to be further improved in 2024.
Strengths: Provides thorough advanced immutability features with SafeMode snapshots, strong MFA, and multiple-administrator validation mechanisms. New software and service features, such as data protection assessment and the ransomware recovery SLA, improve its mitigation and recovery capabilities.
Challenges: Anomaly detection features are adequate for block storage, but proactive ransomware detection needs to be further developed for file storage. Those improvements are on company’s roadmap.
RackTop
Its BrickStor SP is a software-defined data security platform for unstructured data that is fortified with advanced security and compliance features. The solution not only offers file services but also detects and prevents attacks on data before they impact the business.
BrickStor SP active security architecture implements zero-trust principles to protect data. The solution evaluates trust for each file operation in real time, based on client IP, user account, file activity, and other behavioral identifiers, to provide the security and visibility necessary to defend against modern attacks. When BrickStor SP detects irregular or malicious behavior, it can alert the organization’s security or infrastructure team and stop anyone from being able to steal, manipulate, or access the files until the behavior is investigated and mitigated.
The company provides immutable space-efficient snapshots without requiring special reserved space. It offers data protection policies that allow you to apply snapshot and snapshot retention policies to datasets based on the storage profile. This makes it easier to maintain and manage snapshots and demonstrate compliance with regulations and policies.
BrickStor SP proactively detects suspicious and malicious behavior in real time on the controller itself. It doesn’t rely on external servers or the cloud to detect this activity. It has multiple assessors that can be added to and modified at any time using a secure update method. Each assessor looks for specific types of malicious behavior and factors in various things, including the account, operation type, rate of operations, and the way the client connects and is opening files and writing data to the file systems.
It has an advanced incident response workflow, which quickly identifies the suspected attack, including the source account and machines. It provides a workflow and recommended recovery plan for removing and restoring files. Moreover, it doesn’t require an admin to look through versions of snapshots or files to determine the last known good snapshot. The company’s solution analyzes the time of the attack and the last file changes in snapshots to determine the pre-attack copy. BrickStor SP maintains holds on the snapshots around the time of the incident to provide 1mn RPO granularity and ensure no critical data is lost.
Firm’s vault feature provides additional protection for data by creating both a virtual air gap as well as a cryptographic manifest for attestation and chain of custody. Vaults can be created on demand, but once a vault is “sealed,” it can never be modified. Vaulted data is always accessible via a digital twin, which can be either read-only or read-write, but the vaulted data can never be modified. There is no limit on the number of times a twin can be created from a vault environment.
Vendor’s modern user interface can control all the BrickStor storage appliances, forecast future utilization, review data compliance, and manage on-premises and cloud resources.
Strengths: The solution is very well developed and protects vs. ransomware with zero trust built in from the start.
Challenges: Although the company is one of the most feature-rich solutions in this space, it still needs improvement in multiple-controller setup and automation integrations.
StorONE
Its ransomware protection strategy relies on immutable snapshots on its StorONE S1 software-defined storage platform. The solution includes a feature called “anonymous detection,” which performs anomaly detection by identifying unusual patterns, behaviors, or events that deviate significantly from the expected norm. In case of anomalous behavior, customers are instantly notified of unusual activity on one of their volumes.
Company’s immutable snapshots can be created either ad hoc or scheduled with policy-based frequency and retention periods, using either the management interface or API calls. Immutable snapshots can’t be deleted manually while the retention policy is active, and volumes with active snapshots can’t be deleted either. Furthermore, the firm implements multiple-administrator validation for all configuration changes, including retention policies.
The new management interface allows these various policies to be created seamlessly, with a visual understanding of how they overlap and a clear view of how long data is retained. Furthermore, different retention policies and snapshot frequencies can be created per S1 instance.
The company also offers a flash-based S1:Backup appliance targeted at data protection and long-term retention. This appliance is based on StorONE S1 software and implements the same immutability mechanisms. It effectively provides an additional level of protection in case the production StorONE S1 system is impacted. Even if primary and backup data are corrupted by ransomware, the use of immutable snapshots allows users to revert to a safe snapshot taken before the infection occurred.
It’s worth noting that firm’s immutable snapshot technology applies to both file and block volumes. When used with file volumes, the snapshots can be instantly restored to a browsable image at the file level, allowing administrators to verify file integrity and recover a file or subset of files.
Strengths: Offers good capabilities to identify, mitigate, and recover from ransomware attacks, including anomaly detection, instant recovery, and multiple-admin validation.
Challenges: There are several opportunities for improvement around anomaly detection that primarily revolve around visualization dashboards and logging.
WEKA
Its Data Platform is a massively scalable data platform that provides mixed workload capabilities and multiprotocol support (SMB, NFS, S3, POSIX, GPU Direct, and Kubernetes CSI). It is often used in demanding environments requiring low latency, high performance, and cloud scalability.
The platform supplies a proactive, cloud-based monitoring service called WEKA Home that collects telemetry data (events and statistics) and provides proactive support in case of detected warnings and alerts. The commpany can also detect encryption within the underlying storage devices in each storage host by detecting alteration of the block checksum. The solution also supports log forwarding to inhibit tampering by a malicious actor or a rogue administrator.
The multiprotocol nature of the firm’s solution (which includes object storage) and its ability to run natively in the cloud enable it to use snapshots as mitigation against ransomware attacks. This mitigation capability is delivered through its Snap-to-Object feature, which allows data snapshots to be stored in object storage, in either local or cloud object repositories. With Snap-to-Object, data can be protected with immutable object-based snapshots that help safeguard data against ransomware attacks.
WEKA Home can monitor events and alerts across all company’s Data Platform deployments; however, the solution can’t be used to monitor third-party storage repositories. Snap-to-Object is part of the base capabilities of the WEKA solution, and WEKA Home is provided free of charge to customers with a valid support contract.
Strengths: Offers a simple solution that combines monitoring and detection capabilities with immutable object storage snapshots, and the flexibility of using local or cloud-based repositories.
Challenges: Firm’s data protection capabilities are currently limited to WEKA Data Platform deployments only.
6. Near-Term Roadmap
There’s a clear divide among the evaluated solutions in terms of capabilities because many are already mature in providing a broad set of advanced features, including AI/ML-based anomaly detection and proactive remediation.
Implementing proactive threat detection is a possible roadmap direction for less-mature solutions that offer snapshot immutability and/or continuous data protection. However, this largely depends on each vendor’s ability and appetite to commit R&D resources. Given the amount of effort and cost involved, it’s more likely that these solutions’ feature set will remain the same while the vendors seek strategic partnerships with well-established, general-purpose ransomware protection vendors.
Meanwhile, advanced solutions will continue to improve their AI/ML detection and training models. While provided as a part of the primary storage management stack, these solutions will remain adjacent to the storage array itself and may eventually be expanded to support heterogeneous environments. Alternatively, they could be spun off as a standalone solution, free to use with the vendor’s storage platforms but licensed for use with external storage solutions.
7. Analysts’ Take
Although ransomware protection is not new, the increased attack frequency rate is thrusting this discipline more and more into the spotlight. Until recently, data protection, business continuity, and disaster recovery discussions were the primary drivers for ransomware protection solutions.
Organizations were already aware of the need for deep, layered threat protection strategies that implement threat detection and mitigation mechanisms at multiple levels. Similarly, storage vendors acknowledged the ransomware risk and that production data storage systems were often the primary target.
Compared to 2022, several emerging trends such as enhanced immutability and air gapping are reflected in this year’s key characteristics.
Enhanced immutability features are varied and range from policy-based snapshot management to anti-NTP tampering mechanisms. An additional security layer is provided by multiple-administrator validation or similar quorum-based validation mechanisms for sensitive operations such as policy changes or policy deletions. Enhanced immutability features are not necessarily complex to implement and represent an attainable improvement that provides tremendous benefits to customers with moderate R&D efforts.
The other low-hanging fruit, which has been aptly identified by several vendors, is to provide recovery guarantees, recovery SLAs, or a combination of both. These guarantees provide assurance of recovery without fundamentally changing the solution from a technical perspective (an immutable snapshot should always be recoverable). The introduction of ransomware recovery SLAs by which the client gets a loaner storage array and a guaranteed time to recover their primary data is a smart commercial offering that requires minimal R&D investment and delivers immediate value.
In contrast, proactive identification requires a much steeper R&D investment: some companies have decided to take this arduous route in the past 18 months and are now reaping the benefits of these investments by delivering outstanding value to their customers. Moving forward, proactive identification will become a decisive selection factor, especially for file-based storage systems. Although it’s less relevant for block storage solutions, organizations deploying unified storage solutions may want to keep an eye on proactive identification capabilities, particularly for deployment scenarios that include both file and block storage.
By implementing ransomware protection on primary storage systems, storage vendors enable organizations to strengthen their security posture with proactive identification and mitigation. The most advanced ransomware protection primary storage solutions ensure that primary data is minimally impacted by ransomware attacks, guaranteeing a normal flow of business operations while mitigating the consequences of financial, regulatory, and reputational impact.
Furthermore, ransomware protection on primary storage systems – and its maturity – allows storage vendors to differentiate against their competition and create new business opportunities.














 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

