Report for File-Based Primary Storage Ransomware Protection
Leaders being Racktop, Cohesity and Nutanix
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on September 19, 2022 at 2:02 pmThis report, published on September 7, 2022, was written by Max Mortillaro and Arjan Timmerman, independent industry analysts, GigaOm.
GigaOm Sonar Report for File-Based Primary Storage Ransomware Protectionv1.0
An Exploration of Cutting-Edge Solutions and Technologies
1. Summary
Ransomware is a specific type of malware that encrypts data assets on primary storage systems-including file shares, databases, disk partitions, data volumes, backup systems, and repositories-making them inaccessible unless the victim pays an extortion fee. It is highly optimized to spread across networks, organizations, and infrastructure systems through methods similar to trojan attacks. The ransomware payload is embedded in a file that looks legitimate and is triggered by an unsuspecting user opening the infected file. Usually, it will spread across the environment by taking advantage of user credentials, as well as documented and undocumented exploits, bypassing the limited access scope of a user. As such, ransomware protection is a transversal, cross-stack topic across organizations.
Ransomware attacks can impact file- and block-based primary storage solutions alike:
• File-based ransomware attacks are the most pervasive. Advanced file-based ransomware implementations use a combination of techniques to remain unnoticed and spread silently. For example, they start encryption activities a few weeks or months after a system has been infiltrated, or they first target dormant files that haven’t been accessed for a significant time.
• Block-based ransomware attacks, while less common, can be even more damaging. In this case, ransomware encrypts entire data volumes, making recovery much harder than it is for file-based attacks. The entire volume must be recovered, offering less granularity and fewer recovery prioritization options than for file-based recovery activities. These attacks, however, are quicker and easier to detect because once a volume is encrypted, all R/W operations become impossible.
This report focuses on ransomware protection solutions available for file-based – or NAS – primary storage systems, while a sister report covers solutions for block-based primary storage.
Although dedicated out-of-band ransomware protection solutions exist, organizations should not underestimate the benefits of in-band ransomware protection capabilities embedded in NAS solutions. The most effective mitigations include a combination of in-band and out-of-band capabilities, but for smaller businesses or cost-conscious organizations, NAS ransomware protection solutions constitute an important first line of defense.
Benefits of ransomware protection on NAS solutions include:
• Faster recovery from a ransomware attack than backup restores can provide, usually measured in minutes instead of hours or days, thanks to snapshots. This is particularly crucial for mission-critical applications that can’t withstand prolonged downtimes.
• Greater ease of use as reverting to a healthy snapshot takes considerably less effort than identifying and orchestrating data recovery from a data protection platform.
• Cost-effective protection and recovery operations: NAS ransomware protection solutions are usually provided at no cost and deliver a very effective protection layer. Furthermore, fast local recovery from ransomware is cheaper than recovery from data protection systems, both from a recovery time and a human effort perspective. In addition, organizations avoid paying any potential egress transfer fees when restoring from the cloud.
How We Got Here
Ransomware attacks have become a prevalent and persistent threat for all organizations across all industries and sizes of business. While these attacks frequently made headlines a few years ago, they’ve now become so widespread that only the most spectacular cases are mentioned in the news media today.
Organizations assess business risk by evaluating the probability of an event occurring and correlating this probability with the impact (the extent of possible damage), usually through a risk assessment matrix. The impact can be diverse, ranging from negligible to widespread, but regardless of the physical manifestation, outcomes are generally summed up in 3 categories: financial (loss of revenue), regulatory (increased scrutiny, fines, and, eventually, the loss of license for regulated businesses), and reputational (loss of trust from customers).
Ransomware is particularly concerning for organizations because it combines a high probability of happening with a severe and widespread impact, not only in terms of locations and systems affected but also in terms of damage. It can bring businesses and government agencies to their knees, forcing them to choose between paying a hefty ransom or risk losing production capacity and revenue for weeks, if not months.
It does not discriminate among infrastructure layers; once in, it will attempt to encrypt all of an organization’s assets within reach, which is why proper segmentation of access and networks is important. Organizations usually implement several data protection layers, including data protection (backups and DR), security at the network layer, and authentication mechanisms to reduce the attack surface.
However, relying solely on backups should be avoided for the following reasons:
• Primary data is the most up-to-date data repository available in the organization. Large enterprises can have a significant delta between production data and backups, especially if the data has elevated change rates.
• Losing primary data and having to restore it from data protection platforms is a time-intensive process, limited by the throughput of the backup media and network bandwidth, especially if protected data resides on the cloud.
• For cloud-based data protection, data retrieval could incur egress transfer fees, which can add up quickly as more data and systems need to be recovered.
Because primary data is the first point of impact for ransomware attacks, it’s advisable to implement primary storage solutions that incorporate ransomware protection. Timely identification, alerting, and mitigation are preferable to dealing with the aftermath of a ransomware attack and its severe impact from a financial, regulatory, and reputational perspective.
2. Overview
To briefly recapitulate, primary storage ransomware protection solutions emerged in response to the growing prevalence and damaging impact of ransomware attacks. These attacks focus on encrypting data at rest that resides on primary storage systems, including file shares, databases, data volumes, and disk partitions-for example, in VMs. The most sophisticated ransomware also goes one step further and actively targets backup systems and repositories as well to cause maximum damage.
This report focuses on ransomware protection capabilities present in NAS systems.
NAS are prone to ransomware attacks because they present all the characteristics that facilitate a ransomware attack, including:
• Primary point of storage for collaboration use cases broadly used by human operators within the organization.
• Primary storage target for many data asset types, regardless of their criticality.
• Shared storage, usually accessible by numerous individuals across many geographic locations.
• Broad range of types and large numbers of files accessible by many individuals, therefore accessible by any malicious process running on their endpoints.
• Lax or nonexistent permissions on certain shares and folders.
Without proper controls (for example, segmentation of data, least-privilege access, and stringent permissions), file storage repositories become easy targets for the uncontrolled spread of ransomware.
Main Components
The goal of ransomware protection on primary storage is to act as the first line of defense by mitigating threats and ensuring primary data remains protected, thus ensuring continuity of operations. Primary storage solutions can provide ransomware protection in various ways, from very simple capabilities to the most advanced implementations.
Immutable snapshots provide the most basic level of protection. These allow administrators to revert to a healthy state if data is compromised by ransomware. While foundational for ransomware protection, this feature is reactive and doesn’t provide proactive insights. It’s only after the environment has been hit and the ransomware detected that administrators can use immutable snapshots to recover from the attack.
Combining immutable snapshots with other techniques, such as replication, provides an intermediary level of protection. In this case, snapshot data is replicated to a dedicated, isolated system or to the cloud. Additional capabilities, such as basic detection and snapshot recovery orchestration, may also be included.
The most advanced implementations provide sophisticated ransomware identification algorithms trained using AI/ML models. They’re able to analyze a broad range of patterns and anomalous behaviors and correlate seemingly isolated incidents to identify potentially harmful scenarios. These detection patterns include usual activity times in a given geographic area, data types typically accessed (including user access patterns), as well as large-scale file operations across folders and shares. In addition, advanced solutions implement proactive mitigation strategies, such as the identification of systems and accounts that are the source of these changes, the ability to revoke access of potentially impacted users and systems, and the possibility of cutting off access to parts or all of the affected file systems. Finally, these solutions integrate with monitoring and AI operations (AIO/s) platforms, providing comprehensive alerting and active mitigation options.
Ransomware creators implement various techniques to avoid immediate detection. For example, ransomware can make its way into an organization’s environment but stay dormant for weeks or months. It can also perform staggered activities, affecting only a few files at a time, usually those that haven’t been accessed for months or years. However, this focus on old files, while unnoticed by humans, is easy for the storage platform to identify.
With the growth of ransomware protection solutions and the increased focus on proactive monitoring, the concept of encrypting old files first in an indiscriminate manner is losing its appeal and may make room for random patterns that are more difficult to identify. On the other hand, AI-based ransomware protection solutions are regularly updated and trained to catch up with new threat models and identify them.
Market Segment
To better understand the market and vendor positioning, we assess how well NAS solutions with integrated ransomware protection are positioned to serve specific market segments (Table 1). Note that we’re only looking at ransomware capabilities offered by primary storage vendors, not at dedicated, standalone ransomware protection solutions.
• SMB: In this category, we assess solutions on their ability to meet the needs of organizations ranging from small businesses to medium-sized companies, including departmental use cases in large enterprises. For these use cases, the solution should provide a turnkey experience and a complete feature set suited for the IT generalist. The solution should compensate for the limited resources of these organizations and the unavailability of dedicated personnel, whether IT specialists or information security experts.
• Large enterprise: Here, offerings are assessed on their ability to support large and business-critical projects. Optimal solutions in this category will focus on the feature set depth and integration with existing enterprise tools, such as data protection solutions, information security tools, AIO/s, and ITSM platforms. Scalability and flexibility are key to successful enterprise adoption.
Table 1. Market Segment

3. Considerations for Adoption
The purchase drivers for adopting ransomware protection on NAS solutions are very clear. The only potential downside is that a storage system embedding advanced ransomware protection may be more expensive than a storage system without such capabilities. On the other hand, the benefits are so overwhelming that organizations should seriously consider whether purchasing a storage solution without ransomware protection capabilities makes sense.
Prospective customers should carefully consider the following when evaluating solutions: first, how the primary storage ransomware protection fits within their overall security, threat, and ransomware protection posture; and second, how the solution integrates with their broader threat mitigation strategy.
A primary storage solution that provides only immutable snapshots as a ransomware protection layer would be acceptable for an organization that has invested in advanced, dedicated ransomware protection solutions. However, this would be insufficient for an SMB that can’t afford the same investment in a dedicated ransomware solution.
Similarly, a large organization with a heterogeneous storage infrastructure might question the benefits of a deeply integrated and advanced ransomware protection solution that is proprietary to a single storage vendor.
Another consideration is the scope of a given solution compared to the broader infrastructure footprint. If the customer manages other storage types (block storage, for example) and one vendor’s solution supports both file and block systems, this could be an advantageous choice for the organization.
In any case, determining the current security posture of an organization, where it plans to go, and the available budget will help further refine the appropriate adoption criteria.
Key Characteristics for Enterprise Adoption
Here we explore the key characteristics that may influence enterprise adoption of the technology based on attributes or capabilities offered by some vendors but not others. These criteria will be the basis on which organizations decide which solutions to adopt for their particular needs.
These key characteristics are:
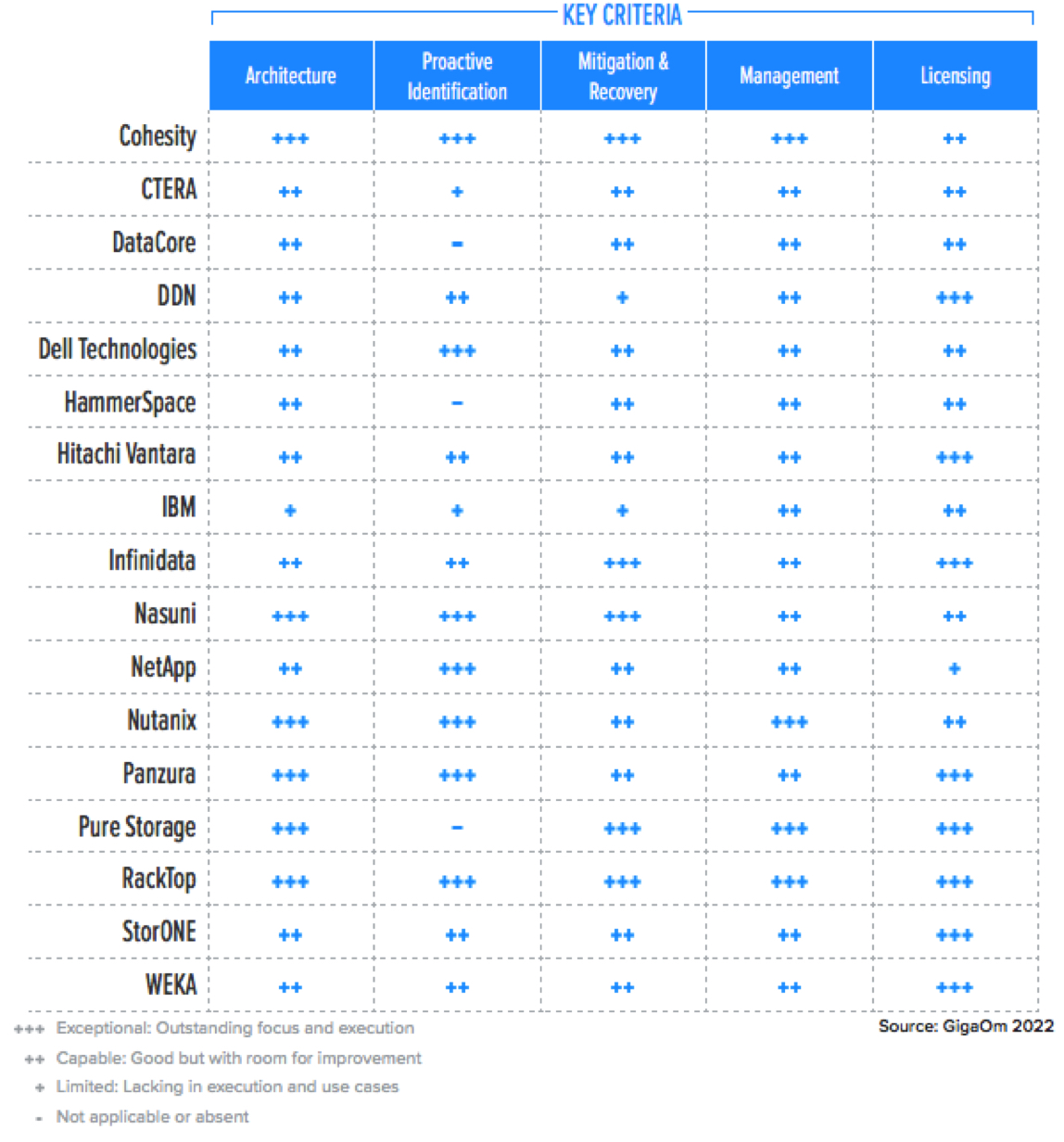
• Architecture
• Proactive identification
• Mitigation and recovery
• Management
• Licensing
Architecture
The design, implementation, and feature set of ransomware protection solutions can impact scalability, performance, and efficiency. Solutions tightly embedded within the storage platform will provide immediate results but will lack the kind of global view that is better able to identify anomalous patterns happening either at scale or in specific locations.
Proactive Identification
Basic ransomware protection features such as snapshots and CDP are now taken for granted. Ransomware infection patterns are nearly imperceptible to IT personnel, who often realize the extent and impact of a ransomware attack only after it’s too late to react. Advanced ransomware protection systems are trained on ransomware behavioral patterns that can identify anomalous behavior by analyzing file system changes in real time.
Mitigation and Recovery
Although timely identification of infection patterns is crucial, alerting is not sufficient. The solution should implement techniques to isolate encrypted data and contain the spread; for example, by terminating active connections to the file system or temporarily restricting access. Similarly, it must implement methods to recover the impacted data easily.
Management
Monitoring and alerting capabilities, and the ability to visualize threats and their impact, are essential. The solution should include a management interface with proactive alerting capabilities and integrate with enterprise system management solutions, AIO/s, and IT service management (ITSM) tools.
Licensing
Regardless of the architecture and deployment model, some ransomware protection features are included in the storage solution feature set at no cost, while more advanced solutions might be licensed separately. However, some vendors offer advanced protection as an integral part of the storage system.
Table 2 shows the principal features that can affect the adoption of ransomware protection for NAS systems, and how well each is implemented in the solutions assessed in this report.
Table 2. Key Characteristics Affecting Enterprise Adoption
4. GigaOm Sonar
It provides a forward-looking analysis of vendor solutions in a nascent or emerging technology sector. It assesses each vendor on its innovation and architecture approach while determining where each solution sits in terms of enabling rapid time to value (Feature Play) vs. delivering a complex and robust solution (Platform Play).
The GigaOm Sonar chart (Figure 1) plots the current position of each solution vs. these three criteria across a field of concentric semi-circles, with solutions set closer to the center judged to be of higher overall value. The forward-looking progress of vendors is further depicted by arrows that show the expected direction of movement over a period of 12 to 18 months.
Figure 1. GigaOm Sonar for File-Based Primary Storage Ransomware Protection
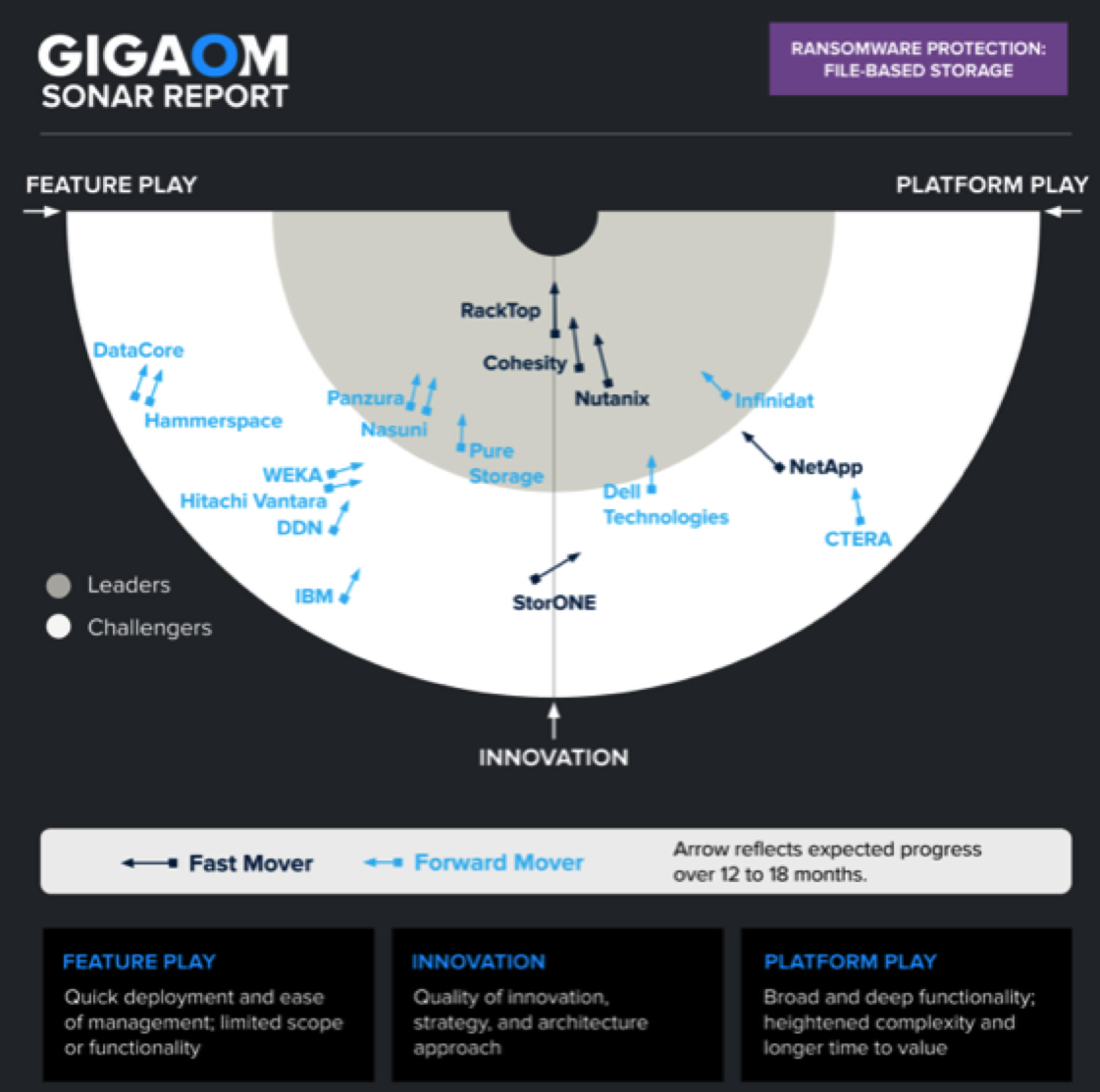
As you can see in the Sonar chart in Figure 1, ransomware protection solutions for file storage are spread across the entire chart; however, several groups can still be identified.
A first group consists of Leaders at the center of the chart, either on the Innovation axis or close to it. These offerings provide a very fast time to value without compromising on the breadth of the solution. RackTop provides a no-compromise approach to ransomware protection with a strong zero-trust foundation and a feature set that will continue to deliver long-term value to organizations. Cohesity is very well positioned along the Innovation axis: Besides providing outstanding ransomware protection for its file system, the platform also delivers strong value in areas adjacent to ransomware protection, such as data protection and data management. Nutanix follows closely with a different approach in ransomware detection, yet it delivers overall very good and balanced capabilities.
Still, on the right side of the chart and within the Leaders tier, Infinidat offers a complete ransomware protection solution with InfiniGuard Cyber Recovery. Although the solution is simple to deploy and operate and has a fast time to value, Infinidat is placed in the Platform-Play area to highlight the strategic character of such an investment.
On the left side of the chart, the Leader group consists of 2 distributed cloud file storage solutions, Panzura and Nasuni, followed by Pure Storage.
Panzura offers a very nice set of proactive detection, mitigation, and recovery capabilities, as well as peripheral insights that can help further, although automated recovery orchestration needs to be developed.
Nasuni delivers a complete ransomware protection solution that includes proactive detection, recovery, and mitigation with plans for automated recovery orchestration. Although each of these two solutions offers a slightly different set of capabilities (which Panzura includes in the base price and Nasuni offers as a paid add-on), the capabilities and outcomes are very similar and offer outstanding value to customers.
Pure Storage follows closely: Its SafeMode snapshot feature is complemented with commendable zero-trust capabilities and would achieve an even better rating if it wasn’t for its lack of advanced proactive detection capabilities, which are currently in the roadmap for Pure1.
The other vendors are sparsely populated across the two areas of the chart. On the right side of the Innovation axis, solutions with a more strategic focus include Dell, NetApp, CTERA, and Hitachi.
Dell Technologies is pictured moving from the Challengers area towards the Leaders area, provided that it commits to its roadmap: It has built comprehensive ransomware protection capabilities for its PowerMax storage platform, available with both block and file volumes. On PowerScale, the company relies on integration with Ransomware Defender, a separately licensed solution developed by Superna, a company in which Dell invests. Capabilities are not fully available across the entire portfolio yet, an area for improvement.
While NetApp is in the Challengers area, it has a very ambitious roadmap and a good set of existing capabilities across multiple storage systems and management platforms. Although the current landscape is heterogeneous, the company is innovating rapidly and offers potential for consolidation and major improvements in the next 12 to 18 months.
CTERA offers foundational capabilities with immutable snapshots but currently relies on external integration with Varonis for ransomware protection. Still, it’s worth noting that the solution also embeds a built-in antivirus feature.
Last in this area, Hitachi offers some 3rd-party licensed capabilities, but no major breakthrough is expected as the company is instead focusing on block and object ransomware protection.
StorONE is alone in the middle of the Challengers area, transitioning from the Feature-Play area toward the more strategic players. It currently offers a well-balanced solution and has a good roadmap to further improve its feature set.
Finally, Challengers in the Feature-Play area consist of 2 sub-groups: one with WEKA, DDN, and IBM; a second with Hammerspace and DataCore.
In the first sub-group, WEKA leads with its Snap-To-Object feature, which enables immutable snapshots to be stored locally and in object storage. WEKA Home also provides cloud-based anomaly detection to inform customers of changes in their system; however, the solution doesn’t yet support monitoring of third-party storage repositories.
DDN also offers immutable snapshots and cloud-based monitoring, but it has no proactive ransomware detection capabilities and relies instead on indirect evidence via monitoring of ransomware-related metrics.
In the file storage space, IBM offers its Spectrum Scale parallel file system. Although not initially designed to handle general-purpose file workloads, the solution offers granular control over immutability settings and indirect monitoring of ransomware-related I/O metrics.
The 2nd sub-group consists of 2 vendors, Hammerspace and DataCore. DataCore’s vFilo solution is based on the Hammerspace solution, so both share the same opportunities and challenges. The immutability feature set is very good, but native proactive detection capabilities and recovery orchestration are missing.
5. Vendor Insights
Cohesity
It offers a compelling solution that meets data protection, cyber resiliency, and data management challenges in hybrid cloud scenarios with its Helios platform. It offers sophisticated data protection via SmartFiles-a software-defined file and object service within the Helios platform-that provides ML-based early detection of attacks by monitoring data changes vs. normal patterns (using several metrics) and measuring abnormal activity vs. the usual activity baseline.
The firm also supports immutable snapshots and protects vs. attempts to modify them, a capability at the core of its SpanFS file system. The solution implements rapid recovery that leverages fully hydrated copies, local search, ML-based recommendations, and patented technologies to recover many VMs instantly, perform non-disruptive restores of Oracle databases, and reinstate instant NAS access. To further strengthen immutability, the company introduced Fort Knox, a strongly secured, isolated cloud air-gap immutable storage solution that is delivered as a service.
It has additional protection measures and anti-tampering techniques, preventing, for example, NTP attacks. These attacks usually trick the servers and data protection systems into moving time forward to artificially expire immutability flags on locked datasets. Cohesity protects vs. such attacks by never moving the time forward more than 10 minutes per 14-day period, even if time servers ask to jump forward.
Another differentiator is a strong zero-trust multifactor authentication (MFA) module with quorum-based approval for sensitive actions in the environment, such as changing protection policies. Organizations can define which individuals can approve sensitive actions. Then, any authorized individual launching a sensitive action will trigger an approval workflow requiring quorum before the action goes into effect. The quorum-based approval feature offers full granularity and permits the creation of multiple groups, each covering specific options, allowing full customization based on an organization’s internal policy and security posture.
These capabilities are easy to manage and are provided through a single management pane. The features can also be used in the context of data protection components present in the Cohesity platform.
Strengths: Offers a very strong cyber-resiliency approach that includes proactive ML-based detection, on-premises and cloud-based immutability capabilities, and strong zero-trust and anti-tampering features. The platform approach allows Cohesity to thrive not only with file-based ransomware protection but also with data protection and, to a lesser extent, data management.
Challenges: Platform covers a broad set of workloads and capabilities, and it might not always appeal to organizations seeking simple solutions.
CTERA
It presents a distributed cloud file storage platform built around its Global File System (GFS), which can reside in the cloud as well as in on-premises infrastructure. Organizations can access GFS through 3 components: a CTERA Edge Filer gateway (an SMB/NFS network filer, which can be deployed centrally or at edge locations with a compact HC100 Edge Filer), the CTERA Drive (a desktop/VDI agent), or the CTERA mobile application.
To help defend vs. ransomware threats, the firm implements several techniques: the solution uses read-only immutable snapshots and continuously replicates those snapshots to the cloud on immutable object storage. Using CTERA’s “instant DR” feature, the snapshots can be instantly recovered from the cloud so that users can immediately access the data as it is being recovered in the background. Whenever a file that was not yet recovered is accessed, it is pulled from the cloud in real time, prioritizing data recovery based on file usage patterns (downloading actively used files first).
For the most security-sensitive organizations, the company also supports AWS cross-account bucket replication to air-gap data in case administrative credentials are compromised. Other features include a zero-trust architecture that prevents exploitation of edge filers to access central data, and multi-factor authentication for administrator access and validation of certain sensitive operations.
There are no native proactive identification capabilities; however, 3rd-party integration with Varonis allows organizations to monitor and analyze logs, assist with data classification, and identify risky permission settings. A single instance of Varonis is required for an entire organization using CTERA, mitigating the addex complexity caused by working with a third-party vendor. Also worth mentioning is the presence of a dual integrated antivirus: virus scanning is performed both on edge filers and in the cloud. Finally, organizations can forward CTERA logs to their SIEM platform through syslog forwarding.
Firm’s immutable snapshots and the built-in antivirus are part of the solution’s feature set and do not incur extra licensing fees. Varonis integration works under a BYOL (bring your own license) model.
Strengths: Immutable snapshots deliver foundational ransomware recovery capabilities. Although this is the only built-in ransomware protection feature, integration with Varonis provides customers with an advanced solution to protect vs. ransomware.
Challenges: It has no proactive detection capabilities unless used with the third-party Varonis solution.
DataCore
It offers file storage capabilities through vFilO, a SDS solution that is based on Hammerspace technology. The feature set is similar to the one offered by Hammerspace, except for the branding and management interface aspects.
To protect data vs. ransomware attacks, vFilO primarily delivers immutability features that are combined with third-party detection capabilities. There is no proactive detection: organizations can either create ad-hoc alerts on specific metrics commonly indicating a potential attack (such as data change rates, drops in data efficiency such as compression and de-dupe, and so forth), and can also make use of vFilO’s automated antivirus scanning through a third-party integration that leverages the iCAP protocol, a feature that must be configured separately.
On the remediation side, vFilO implements immutable file shares with global snapshot capabilities as well as an undelete function and file versioning, allowing users to revert to a file version not affected by ransomware-related data corruption.
Immutability functions are base features of the solution, but the third-party antivirus integration must be licensed separately, as DataCore only provides the integration framework.
Strengths: vFilO implements a solid set of immutability features.
Challenges: The solution faces the same challenges as Hammerspace: lack of native proactive detection capabilities and lack of recovery orchestration features. As a rebranded solution, DataCore vFilO depends on updates made by Hammerspace.
DDN
Among its storage solutions, the Intelliflash platform delivers unified file and block storage capabilities and includes features to protect vs. ransomware attacks: IntelliCare for detection and Intelliflash immutable snapshots for remediation.
From a detection perspective, Intelliflash leverages the IntelliCare Cloud Analytics platform to identify unusual storage growth (which can often indicate ransomware activity) and generate alerts.
If a ransomware attack is confirmed, Intelliflash snapshots can be used to rapidly revert to a prior healthy state. The snapshots can be scheduled and enabled from Intelliflash’s management interface, with capability to land snapshots on-premises, in the cloud, or both, including options to store data at multiple locations.
Both Intelliflash snapshot capabilities and the IntelliCare Cloud Analytics platform are part of the base company’s feature set.
Strengths: Provides a basic set of ransomware protection features on its Intelliflash platform, including basic monitoring capabilities and immutable snapshots.
Challenges: Detection capabilities are limited and indirect. No recovery orchestration.
Dell Technologies
It delivers ransomware protection through a combination of storage array capabilities (read-only snapshots) and CloudIQ-the company’s AIO/s management platform that supports a broad range of Dell Technologies products-and through integration with third-party software that specializes in ransomware protection and other security functions. Four primary storage solutions offer file storage capabilities: PowerScale, Dell’s scale-out file system based on OneFS, and three unified block and file storage arrays, the PowerMax, PowerStore, and PowerFlex appliances.
PowerScale’s native snapshot functionality can be leveraged as part of a ransomware protection strategy. The snapshots are read only and can be anchored at the filesystem, share, folder, subfolder, or individual file level. OneFS RBAC can separate the ability to create and delete snapshots to separate user types, and delete snapshots can be removed for all users except the root account if desired. OneFS native change-tracking functionality also allows an administrator to identify any altered files by comparing the active filesystem to a snapshot or a snapshot to other snapshots. OneFS snapshots can also be replicated to separate PowerScale units or S3-based object stores.
To detect ransomware and orchestrate mitigation and recovery activities, the company relies on Superna Ransomware Defender along with several optional plug-ins. The Superna software suites have been developed specifically for PowerScale and ECS and are run externally to the storage array to provide real-time ransomware detection, response, and mitigation activities. Ransomware Defender is scalable to multiple arrays and sites and covers the PowerScale and ECS platforms. Ransomware Defender proactively monitors these platforms for threats and can trigger automated response scenarios such as locking users out, taking snapshots, suspending schedule replication or copy jobs, and more.
From a recovery orchestration standpoint, Ransomware Defender can identify files impacted by a ransomware attack and offer targeted data recovery, making recovery faster and more efficient. Threat responses will be orchestrated among all systems at all sites that are monitored by Ransomware Defender.
Ransomware Defender has other security and protection functions, such as live wiretap gen for inspection of client real-time activity. It can also simulate penetration tests and execute scheduled failover tests for any replication sessions for PowerScale. Optional plug-ins for Ransomware Defender include a geo-fencing feature, a zero-trust API, data target integration with network appliances and devices, and an isolated vaulting function.
The Superna solution requires separate licensing, either per storage node, per cluster, or on a subscription basis.
PowerMax, PowerStore, and PowerFlex file services are provided by a common engine known as SDNAS. On the PowerMax platform, proactive ransomware protection capabilities can be delivered through CloudIQ. PowerMax provides telemetry data to CloudIQ in near real time, which monitors and detects anomalies in the observed client behavior, assesses adherence to security baselines, and identifies incidents such as potential ransomware attacks. Alerts are generated and pushed to administrators through various methods and can be integrated with ITSM and SIEM platforms to automatically create incidents and initiate investigation activities.
All SDNAS snapshots are natively immutable (read-only), and all SDNAS systems, along with PowerScale OneFS, support the Common Event Publishing Agent (CEPA) service, which allows integration with third-party solutions that specialize in ransomware defense and detection, such as Netwrix StealthDEFEND or Varonis DatAdvantage.
Dell also offers ransomware protection for all of its storage platforms, block and file, via an integrated datacenter response sold as the PowerProtect Cyber Recovery solution. This solution is a highly secure repository that can identify infected content and securely recover the data to the original platform or a clean room system for further forensic inspection. PowerProtect Cyber Recovery is platform independent and is sold separately from PowerScale, PowerMax, PowerStore, and PowerFlex.
Strengths: For file storage, offers a balanced set of ransomware protection capabilities for theirPowerScale platform, combining proactive detection and immutable snapshots with additional recovery orchestration capabilities on PowerScale.
Challenges: Two very distinct approaches to ransomware protection-consolidation of capabilities via CloudIQ or integration of Superna technology-could be an opportunity to simplify ransomware protection operations in environments where various Dell storage platforms coexist.
Hammerspace
Its Global Data Environment is a SDS and data management solution, a global file system that allows organizations to build a scale-out file system within a datacenter or cloud, as well as to create hybrid clouds that scale across multiple sites. The global data environment can span multiple on-premises geolocations and public cloud platforms, providing applications and users unified access to the organization’s entire data set.
To protect data vs. ransomware attacks, the company primarily delivers immutability features combined with third-party detection capabilities. There is currently no proactive detection capability, although Hammerspace has all the foundational elements to make this happen in an eventual release.
Customers can take advantage of firm’s automated antivirus scanning directly or through a 3rd-party integration with the customer’s antivirus solution (via the iCAP protocol). It’s worth noting that the firm implements floating IP addresses for its nodes, obfuscating the back-end infrastructure and making it more difficult for an attacker to discover on which nodes the data is stored.
On the remediation side, the company implements immutable file shares with global snapshot capabilities, both on-premises and in the cloud. Snapshots can also be restored to a different Hammerspace system if the source system is compromised. Two other mitigation functions are undelete and file versioning, allowing users to revert to a file version not affected by ransomware-related data corruption.
Immutability functions and built-in antivirus scanning are part of the solution’s basic feature set and do not require additional licensing.
Strengths: The solution sports a good set of mitigation and recovery features with immutable snapshots on-premises and in the cloud, flexible restores, as well as undelete and file versioning.
Challenges: Has limited functionality due to lack of native monitoring and detection capabilities. It has no orchestrated recovery features.
Hitachi Vantara
It offers file storage capabilities through the WEKA Data Platform, a SDS solution based on WEKA technology. The feature set is similar to that offered by WEKA, except for the branding and management interface.
The WEKA Data Platform is a massively scalable single data platform that provides mixed workload capabilities and multi-protocol support (SMB, NFS, S3, POSIX, GPU Direct, and Kubernetes CSI). It is often used in demanding environments that require low latency, high performance, and cloud scalability.
It supplies a proactive cloud-based monitoring service called WEKA Home that collects telemetry data (events and statistics) and provides proactive support in case of detected warnings and alerts. WEKA can also detect if the underlying storage devices in each storage host have been subjected to encryption by detecting if the block checksum has been altered. The solution also supports log forwarding to inhibit tampering by a malicious actor or a rogue administrator.
The multiprotocol nature of the WEKA solution (which includes object storage) and its ability to run natively in the cloud enable it to use snapshots as mitigation vs. ransomware attacks. This mitigation capability is delivered through its Snap-to-Object feature, which allows data snapshots to be stored in object storage, either on local or cloud object repositories. With Snap-to-Object, data can be protected with immutable object-based snapshots that help safeguard data vs. ransomware attacks.
WEKA Home can monitor events and alerts across all WEKA Data Platform deployments; however, the solution can’t be used to monitor third-party storage repositories. From a licensing perspective, Snap-to-Object is part of the base capabilities of the WEKA solution, and WEKA Home is provided free of charge to customers with a valid support contract.
Strengths: Thanks to its partnership with WEKA, Hitachi offers a straightforward solution that combines monitoring and detection capabilities with immutable object storage snapshots and the flexibility of using local or cloud-based repositories.
Challenges: From an ecosystem standpoint, the solution is limited only to WEKA deployments; and from a development aspect, Hitachi is dependent on the WEKA Data Platform’s roadmap.
IBM
It supports ransomware protection capabilities on its Spectrum Scale parallel file system with the immutable filesets feature, which implements immutability at the file level, providing append-only capabilities that are available both via SMB and NFS protocols.
Immutability of files is controlled through file-system-level attributes configured either through Spectrum Scale’s Integrated Archive Manager (IAM) or standard POSIX commands. Spectrum Scale immutability supports multiple IAM modes that allow granular control of immutability attributes on a given fileset. The solution’s capabilities are very similar to the NetApp SnapLock feature, cited in IBM Spectrum Scale documentation (IAM even implements a SnapLock-compatible IAM mode).
Early warning signs of an attack can be provided by IBM Storage Insights or Spectrum Control. Both solutions can analyze current I/O workload vs. a previous usage baseline and help provide indications that an attack is in progress. Organizations can set up alerts that indicate an attack may be happening by combining multiple triggers. For example, a sudden drop in data reduction efficiency could indicate vast amounts of data getting encrypted, rendering de-dupe and compression ineffective. The company also recommends monitoring the write change rate for deviations and anomalies, as well as further integration with SIEM platforms (such as IBM QRadar) for better visibility.
There are currently no particular orchestration or proactive snapshot capabilities. Immutable filesets is a built-in feature in Spectrum Scale that doesn’t require specific licensing.
Strengths: Although not initially designed to combat ransomware, Spectrum Scale offers granular control over immutability features with multiple immutability modes.
Challenges: The primary driver for immutability on Spectrum Scale was intended for long-term retention and archival of data. Currently, the solution is very limited; the use of immutability for ransomware use cases needs to be further developed and simplified.
Infinidat
It boasts a modern, AI-based hybrid storage architecture that delivers a no-compromise feature set with compelling $/GB and $/IO/s figures. To achieve this, its InfiniBox storage system takes advantage of a data path designed around a combination of DRAM, SSDs and HDDs associated with sophisticated AI-based caching technology to optimize data placement.
Ransomware protection is delivered through the InfiniGuard solution, which offers modern data protection, backup, DR, and BC features. InfiniGuard provides backup and recovery performance at scale, covering all data protection needs, and is enhanced with InfiniSafe cyber recovery technologies to ensure the customer is ready in the event of a cyberattack. While originally announced on the InfiniGuard platform in February 2022, InfiniSafe was expanded to the InfiniBox and InfiniBox SSA platforms in April 2022.
Branded InfiniGuard CyberRecovery, this capability provides immutable snapshot copies of source data sets that incorporate logical air-gapping-both local and remote. When a customer has a cyberattack, they can move the copies into a secure, fenced network to check for malware or ransomware. Once a known good copy of the data set is identified, the customer can make a near-instantaneous recovery of the known good copy in minutes for petabyte-scale backup datasets.
For the InfiniBox and InfiniBox SSA platforms, the firm announced the InfiniSafe Cyber Storage guarantees in August 2022. Not only will Infinidat guarantee that the immutable snapshot is immutable, but it will also guarantee recovery of the immutable snapshot in one minute or less, regardless of dataset size.
InfiniSafe brings together the key foundational requirements essential for delivering comprehensive cyber-recovery capabilities with immutable snapshots, logical air-gapped protection, a fenced forensic network, and near-instantaneous recovery of backups of any repository size.
Infinidat offerings are focused on customers with very large datasets. In petabyte-scale environments, ensuring fast and secure data is an enormous undertaking, but Infinidat helps customers protect their environments with InfiniSafe technologies, included with the InfiniGuard solution at no additional cost.
An area that requires further attention is delivering better proactive identification.
Strengths: InfiniGuard delivers solid cybersecurity features at no extra cost, allowing customers to quickly and securely restore data, even at scale, in case of an attack.
Challenges: Proactive identification is still limited and needs improvement.
Nasuni
It offers an SaaS solution for enterprise file services, with an object-based global file system as its main engine and many familiar file interfaces, including SMB and NFS. The solution is integrated with all major cloud providers and works with on-premises S3-compatible object stores. Many Nasuni customers implement the solution to replace traditional NAS. Its characteristics let users replace a number of infrastructure components, such as backup, archiving platforms, and more.
Company’s Ransomware Protection is a recently introduced add-on service that delivers in-line detection of live ransomware attacks with up-to-date intelligence on the latest emerging variants, allowing organizations to proactively identify and mitigate ransomware attacks. The service analyzes malicious extensions, ransom notes, and suspicious incoming files based on signatue definitions that are pushed to Nasun Edge Appliances. A next iteration of the solution (in the roadmap) will implement AI/ML-based analysis on edge appliances. Currently, the solution provides up-to-date intelligence on the latest ransomware variants and can report on all impacted files, impacted users, and source IP addresses. Notifications are provided in the Nasuni UI and via email. They can also be forwarded via syslog to external monitoring platforms for further analysis by enterprise-wide security event monitoring solutions used by security operations center (SOC) experts.
On the remediation side, Nasuni Rapid Ransomware Recovery acts as a last line of defense, allowing the recovery of millions of files withins before the attack occurred, with RPO granularity that can go as low as 1mn. The feature takes advantage of firm’s Continuous File Versioning, a built-in capability that protects data as immutable objects with a near-infinite number of recovery points.
The solution is easy to activate and manage and offers comprehensive protection across the entire customer’s Nasuni footprint. Combined with built-in capabilities, such as Nasuni Continuous File Versioning, Ransomware Protection can drastically reduce recovery times from more than 12 hours to less than one hour. As mentioned above, Ransomware Protection is an add-on paid feature.
Strengths: Offers a complete feature set that covers detection and remediation, provided as an easy-to-deploy add-on service.
Challenges: The solution was made available in April 2022, so is not market-proven; meaning there’s not yet customer confirmation or independent verification that the solution works adequately.
NetApp
It implements a comprehensive ransomware protection strategy across its product portfolio, both for on-premises and cloud workloads, with multiple layers of protection. It provides an embedded anti-ransomware capability for primary storage on its appliances (“on-box”) via ONTAP, starting with version 9.10.1. This feature performs workload analysis on SMB and NFS environments and proactively detects and warns about anomalous activities that could be related to ransomware attacks.
Anti-ransomware is designed to address denial-of-service attacks that perform data encryption to extort a ransom. The solution includes ML capabilities and can identify whether data is encrypted or plain text. It also has an analytics engine that can determine whether the data content of a file matches its extension type, whether there is a surge in volume activities related to data encryption, and whether the file presents specific characteristics (such as high data entropy).
The solution is configurable per volume and allows the system to take additional snapshots (on top of already existing or scheduled snapshots) in case abnormal activity is detected. It can either be enabled on new volumes or retroactively added to existing ones. However, when retroactively added: it will only scan new data present in the volume.
NetApp on-box anti-ransomware has specific compatibility requirements and requires a “dry run” initial learning period for the engine to assess workload characteristics and adapt to the customer’s environment. The company recommends a 30-day learning period before switching anti-ransomware protection to active mode.
NetApp Cloud Insights provides additional monitoring capabilities through NetApp Cloud Secure, one of its subcomponents. This component monitors file shares and can also report on potential attacks in progress and automate certain actions via policy (shut off access from compromised accounts, take a preventive snapshot, or do both).
From a mitigation perspective, a locked snapshot (which can’t be deleted by conventional means) is proactively taken when the system suspects an attack is in progress. The administrators can recover to this snapshot if it is confirmed that an attack took place. If, however, the detected event turned out to be a false positive, the admins can mark it as such, and the system will delete the locked snapshot. Since May 2022, the firm has also offered multiple-administrator verification for sensitive operations. This can prevent unauthorized changes made by one person to snapshot and replication policies, immutability settings, snapshot deletion, and more.
The on-box anti-ransomware capability can be combined with other ONTAP features such as FPolicy, snapshot copies, and SnapLock. An additional layer of mitigation and prevention can be used with NetApp Active IQ Digital Advisor. This AIO/s platform includes a Ransomware Defense widget that provides advice on potential risks that could help ransomware propagate and proposes risk mitigation activities, such as enabling FPolicy and more.
The feature can be managed from either ONTAP System Manager or the ONTAP CLI, and it can be configured to be enabled by default on any new volumes that meet required criteria. The use of anti-ransomware capabilities on ONTAP requires the activation of a multitenant key management license, which is not part of the basic subscription.
These capabilities can be extended through the use of complementary cloud-based solutions from NetApp (such as FPolicy on Cloud Volumes ONTAP), which provide various detection and remediation capabilities (Cloud Insights) combined with immutable storage (Cloud WORM). These are, however, not integrated with the on-box anti-ransomware capability described in this document and are more relevant to cloud workloads. Most of the ransomware capabilities can be handled easily through Cloud Insights and ONTAP System Manager.
Strengths: Offers a fully fledged anti-ransomware implementation available on-box, without any additional software, and provides both proactive identification and mitigation capabilities while also being backed by a local ML engine. Active IQ can also help provide ransomware mitigation recommendations across managed systems.
Challenges: The feature requires a specific license to be enabled. Ransomware protection capabilities are currently handled through different layers, providing the company with an opportunity to further integrate and simplify management aspects.
Nutanix
It provides a comprehensive platform with varied storage capabilities beyond its initial HCI scope. The solution, Unified Storage, delivers native file, block, and object capabilities through its suite of products. In the context of primary file storage, the solution delivers these capabilities through the Nutanix Files service.
It implements file-based ransomware protection and mitigation capabilities via integrated data security and analytics features along with Data Lens, a cloud-based (SaaS) data governance service that empowers customers to proactively assess and mitigate ransomware threats.
Recently, the company created Data Lens, an enterprise-grade, SaaS-based data governance platform. Data Lens offers an anomaly-detection engine that monitors data activities such as mass file deletions or permission changes. Administrators can define policies and alerts to get informed of potential threats. The solution allows monitoring of Nutanix Files deployments globally across one or more clusters. Furthermore, Data Lens can baseline normalized cluster behavior across thousands of deployments, providing better anomaly detection capabilities. It comes with zero-day ransomware protection and blocks suspicious files and users in case of a potential attack. Finally, it also embeds 4,800+ up-to-date malware signatures for better malware identification and mitigation.
From a mitigation and recovery perspective, Nutanix Files provides immutable snapshots, preventing tampering and deletion. Those native snapshots make recovery easy, and organizations can also take advantage of a secondary level of immutable storage with Nutanix Objects, which also delivers immutable object storage and support for WORM policies.
By default, the firm also implements hardening features that can be used to prevent ransomware attacks. Adherence to security baselines and monitoring vs. baseline deviations are handled through Nutanix Security Central, a security monitoring and management platform that works across multiple Nutanix deployments. The solution also has strong support for compliance, with several standards supported (FIPS, DoDIN APL, and so forth), and embeds a fully fledged STIG compliance setup.
Nutanix Data Lens is a value-added service to the Unified Platform.
Strengths: Delivers a strong value proposition with proactive ransomware detection and alerting capabilities, security hardening features, and instant data recovery through immutable native snapshots.
Challenges: There is currently no recovery orchestration mechanism.
Panzura
It offers a distributed file storage solution based on its CloudFS file system. This solution works across sites (public and private clouds) and provides a single data plane with local file operation performance, automated file locking, and immediate global data consistency.
Proactive threat identification is handled through company’s Data Services. The solution implements various anomaly-detection mechanisms that are used for ransomware detection and protection. When a suspicious activity that follows ransomware patterns is detected, Data Services can identify, alert, and shut down access to data repositories to prevent further damage.
Ransomware mitigation is handled with a combination of immutable data (a WORM S3 backend; the firm supports a broad range of on-premises and cloud-based object storage solutions), with read-only snapshots taken every 60s at the global filer level, regularly moving data to the immutable object store, and allowing seamless data recovery in case of a ransomware attack. The recovery mechanism is faster than a backup-based recovery from a speed, granularity, and resource use perspective and incurs no storage penalty.
Data Services provides comprehensive auditable information for data stored on CloudFS regarding user activities such as data copy, file and folder creation, file system operations (lock, write, move, read, delete, rename), and changes in attributes and permissions. This information is accessible and can be filtered to refine by audit action and date range or user; the solution can return millions of results in under a second. Data Services can be used to identify impacted files or users and actions that may have impacted files and/or permission sets, helping to narrow the scope of an attack’s potential impact and reach. In addition, firm’s global services team also helps customers to recover from an attack.
The solution is easy to manage through Panzura’s management console. Ransomware mitigation capabilities are baked into the solution and provided at no extra cost. However, Enhanced Ransomware Protection (part of Data Services) that handles proactive threat identification is subscription-based.
Strengths: Implements a solid set of ransomware identification, protection, and recovery mechanisms, with additional peripheral insights that can be useful in identifying and combating vectors for ransomware attacks.
Challenges: There is no automated recovery orchestration mechanism yet; this will soon be included.
Pure Storage
It offers multiple storage products. Among them, FlashBlade delivers unified fast file and object storage capabilities, while FlashArray focuses on block and file storage.
To protect vs. ransomware attacks, the company implements immutable snapshots in both solutions. However, while the data in the snapshots is immutable, the snapshots could be deleted by an attacker with rogue administrative access.
A feature called SafeMode Snapshots, built into both storage array types, locks snapshots and prevents their deletion. On FlashBlade, SafeMode snapshots can be used to create a read-only protected snapshot of a full backup, including the backup and associated metadata catalogs as well.
Instead of the standard deletion process, objects such as volumes or snapshots are destroyed and moved into a staging “destroyed” area for a predefined period (at least 24 hours, and up to 30 days, with Pure Storage recommending at least 14 days of retention). This incompressible timeframe locks any object in the “destroyed” area and prevents it from being wiped until the timer has expired.
SafeMode is built into the storage solution’s OS and enabled by default. The solution includes strong MFA and requires at least 2 authorized contacts (out of 5) to carry out changes to SafeMode configuration along with firm’s support team via a conference call. Each authorized contact is provided with a 6-digit PIN to enhance security. Though this process may seem cumbersome, it ensures maximum security.
SafeMode snapshots are configured through Pure1, firm’s management, analytics, and support platform. Pure1 also can be used to assess whether SafeMode snapshots are enabled across all Pure storage arrays.
Strengths: SafeMode snapshots provide thorough protection and recovery capabilities vs. ransomware attacks by combining strong MFA and identity verification mechanisms with strengthened protection vs. malicious snapshot deletion across file and block products. SafeMode is included in the base feature set, and Pure1 allows organizations to assess global compliance to SafeMode.
Challenges: The solution lacks built-in ransomware detection capabilities.
RackTop
Its BrickStor SP is a SDS solution for unstructured data that is fortified with advanced security and compliance features. It was built by engineers who gained their insight and experience as members of the US National Intelligence community. They transformed that foundational knowledge into a commercial product to enable organizations to protect their data with very tight data security.
Company’s Cyberstorage solution not only offers file services but also detects and prevents attacks on data before they impact the business. With RackTop Brickstor SP, data is safe-and performance, security, and compliance are also taken care of.
BrickStor SP active security architecture implements zero-trust principles to protect data. The solution evaluates trust for each file operation in real time, based on client IP, user account, file activity, and other behavioral identifiers, to provide the security and visibility necessary to defend vs. modern attacks. When BrickStor SP detects irregular or malicious behavior, it can alert your organization’s security or infrastructure team and stop anyone from being able to steal, manipulate, or access the files until the behavior is investigated and mitigated.
myRack Manager is company’s modern user interface (UI). From this single UI, you can control all your BrickStor storage appliances, forecast future utilization, review data compliance, and manage on-premises and cloud resources. myRack Manager is included with BrickStor, and it reduces the TCO by using policy-based management and controls to meet the most critical and burdensome IT challenges, using automation to notify users and enforce policies.
RackTop provides one of the most comprehensive and secure offerings for file storage solutions, with a very broad spectrum of features for ransomware protection. The solution is licensed as a complete package, and it can be used as an appliance or as a VM, which provides flexibility and the ability to utilize this solution on the edge as well.
Strengths: The solution is very well developed and protects vs. ransomware with zero trust built in from the start.
Challenges: Although RackTop is one of the most feature-rich solutions in this area, integration and partnerships with third-party solutions are still limited. At the time of writing, only HPE and IBM partner with RackTop.
StorONE
Its ransomware protection strategy currently relies on using immutable snapshots on its S1 SDS platform. No special steps are required to make a snapshot immutable as it is the default state of StorONE snapshots. The solution includes proactive detection. Customers are instantly notified of unusual activity on one of their volumes.
StorONE immutable snapshots can be created either ad-hoc or scheduled with policy-based frequency and retention periods, via the management interface or API calls. Immutable snapshots can’t be deleted manually while the retention policy is active, and volumes with active snapshots can’t be deleted either.
The new management interface allows these various policies to be created seamlessly, with a visual understanding of how they overlap and a clear view of how long data is retained. Furthermore, different retention policies and snapshot frequencies can be created per S1 instance.
It’s worth noting that StorONE immutable snapshot technology applies to both file and block volumes. When used with file volumes, the snapshots are browsable at the file level, allowing administrators to verify file integrity and recover a given file or subset of files.
Additional features on the vendor’s roadmap for 2022 include partial recovery orchestration and protection vs. NTP server tampering. All current and future capabilities are part of the solution’s standard feature set and come at no extra cost to customers.
Strengths: Offers good foundational capabilities to mitigate and recover from ransomware attacks, with incremental roadmap improvements planned in 2022.
Challenges: Proactive detection capabilities were recently introduced and are yet to prove their efficiency in the field.
WEKA
It offers its Data Platform, a massively scalable single data platform that provides mixed workload capabilities and multi-protocol support (SMB, NFS, S3, POSIX, GPU Direct, and Kubernetes CSI). The platform is often used in demanding environments requiring low latency, high performance, and cloud scalability.
It supplies a proactive cloud-based monitoring service called WEKA Home that collects telemetry data (events and statistics) and provides proactive support in case of detected warnings and alerts. The company can also detect if the underlying storage devices in each storage host have been subjected to encryption by detecting if the block checksum has been altered. The solution also supports log forwarding to inhibit tampering by a malicious actor or a rogue administrator.
The multiprotocol nature of the WEKA solution (which includes object storage) and its ability to run natively in the cloud enable it to use snapshots as a mitigation vs. ransomware attacks. This mitigation capability is delivered through its Snap-to-Object feature, which allows data snapshots to be stored in object storage, either on local or cloud object repositories. With Snap-to-Object, data can be protected with immutable object-based snapshots that help safeguard data vs. ransomware attacks.
WEKA Home can monitor events and alerts across all WEKA Data Platform deployments; however, the solution can’t be used to monitor third-party storage repositories. From a licensing perspective, Snap-to-Object is part of the base capabilities of the WEKA solution, and WEKA Home is provided free of charge to customers with a valid support contract.
Strengths: Offers a simple solution that combines monitoring and detection capabilities with immutable object storage snapshots, and the flexibility of using local or cloud-based repositories.
Challenges: From an ecosystem standpoint, the solution is currently limited only to firm’s Data Platform deployments.
6. Near-Term Roadmap
There’s a clear divide among the evaluated solutions in terms of capabilities: many solutions are already mature in providing a broad set of advanced features, including AI/ML-based anomaly detection and proactive remediation.
Implementing proactive threat detection is a possible roadmap direction for less-mature solutions that offer snapshot immutability and/or CDP. But, it largely depends on each vendor’s ability and appetite to commit R&D resources. Given the amount of effort and cost involved, it’s more likely that these solutions’ feature set will remain the same while the vendors seek strategic partnerships with well-established, general-purpose ransomware protection vendors.
Meanwhile, advanced solutions will continue to improve their AI/ML detection and training models. While provided as a part of the primary storage management stack, these solutions will remain adjacent to the storage array itself and may eventually be expanded to support heterogeneous environments. Alternatively, they could be spun off as a standalone solution, free to use with the vendor’s storage platforms but licensed for use with external storage solutions.
7. Analysts’ Take
Although ransomware protection is not new, the increased attack frequency rate is thrusting this discipline more and more into the spotlight. Until recently, data protection, BC, and DR discussions were the primary drivers for ransomware protection solutions.
Organizations were already aware of the need for deep, layered threat protection strategies that implement threat detection and mitigation mechanisms at multiple levels. Similarly, storage vendors acknowledged the ransomware risk and that production storage systems were often the primary target.
By implementing ransomware protection on primary storage systems, storage vendors enable organizations to strengthen their security posture with proactive identification and mitigation. The most advanced ransomware protection primary storage solutions ensure that primary data is minimally impacted by ransomware attacks, guaranteeing a normal flow of business operations while also mitigating the consequences of financial, regulatory, and reputational impact.
Furthermore, ransomware protection on primary storage systems-and its maturity-allows storage vendors to differentiate vs. their competition and create new business opportunities.













 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

