How to Activate Backup Data in Amazon Redshift Without Restores or ETL
Eon's AWS Redshift integration unlocks backups as queryable tables for analytics and point-in-time insight across your AWS environment
By Philippe Nicolas | January 28, 2026 at 2:00 pmBlog written by Peleg Kazaz, senior product manager, Eon published Jan. 9, 2026
Summary:
- Eon stores database backups as tables stored in Amazon S3
- Eon allows customers to grant Redshift with access to their backups
- Amazon Redshift can query those tables directly as point-in-time datasets
- Teams can analyze historical data instantly with no restores, ETL, or duplicate analytics environments
Because backups already hold any critical data across the organization.
- You answer historical questions without rebuilding environments
- You cut out redundant analytics copies and pipelines
- You work from a single governed source of truth
- You reuse the same datasets for investigations, validation, compliance, and BI
- Instant point-in-time analytics without waiting for restores
- No ETL pipelines or duplicate analytics clusters
- Trusted baselines for audits, investigations, and debugging
- Lower cost by eliminating redundant environments and copies
- Cross-cloud context via Eon’s unified catalog when needed
Click to enlarge
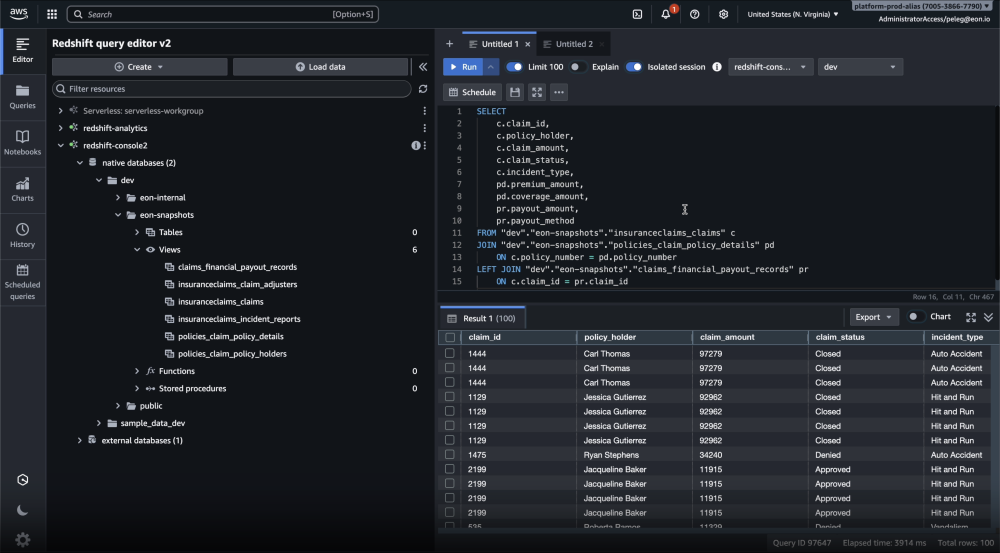
How the Redshift integration works
A simple, AWS-native flow:
- Eon continuously stores backups as deduplicated Hive-partitioned tables
Eon introduces a modern backup format that consists of Hive-partitioned tables stored in Amazon S3 - You choose which backups to share with Redshift
Eon grants read-only access while preserving immutability and governance controls - Redshift queries in place
Amazon Redshift discovers and queries the tables directly in S3
The result: Redshift treats your backups as point-in-time datasets ready for immediate analysis.
What teams do with Redshift-queryable backups
Analytics and BI without rebuilds
Run Redshift queries on historical snapshots to validate changes, investigate incidents, or analyze trends without restoring anything first.
Faster audits and compliance checks
Search and query long-retained point-in-time data directly, instead of waiting on exports or restore jobs.
Operational insight and investigations
Backups provide a clean historical truth for debugging, root-cause analysis, and validating system behavior over time.
How Eon keeps backups usable and secure
Making backups queryable does not mean making them risky.
Baseline protections stay on by default:
- Immutable backups
- Logical air gaps
- Read-only analytics access
- RBAC and audit logs
- Autonomous Cloud Backup Posture Management (CBPM)
Analysts get governed access to historical truth. Security teams stay in control.









 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

