eMemory and PUFsecurity’s PUF-PQC Achieves NIST FIPS 205 and SP 800-208 Certification
Reaching milestone in comprehensive post-quantum cryptography protection
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on January 22, 2026 at 2:01 pmeMemory Technology Inc., provider in embedded non-volatile memory, together with its subsidiary PUFsecurity Corp., a specialist in hardware security silicon IP, jointly announced a technological breakthrough.![]() Their collaboratively developed PUF-PQC Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) hardware-accelerated solution has officially passed the latest standards certification issued by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Their collaboratively developed PUF-PQC Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) hardware-accelerated solution has officially passed the latest standards certification issued by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Following the earlier achievement of FIPS 203 (ML-KEM/Kyber) and FIPS 204 (ML-DSA/Dilithium) certifications, PUF-PQC has now further obtained certification for FIPS 205 (SLH-DSA/SPHINCS+), which specifies stateless hash-based digital signatures, as well as SP 800-208, which defines stateful hash-based signature schemes (LMS/XMSS). This milestone signifies that eMemory and PUFsecurity now comprehensively cover all key PQC standards currently released by NIST.
Building on this foundation, in addition to having already been integrated into the chip designs of leading server management controller (BMC SoC) vendors to support NIST-compliant post-quantum cryptographic security requirements, PUF-PQC has now completed the final piece of the post-quantum security protection framework, further strengthening the company’s leadership position in the global semiconductor security landscape.
Addressing Quantum Threat and Accelerating Security Architecture Transformation
As quantum computing technologies continue to advance at an exponential pace, the public-key cryptographic systems underpinning today’s global digital economy – RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman) and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) – are increasingly exposed to the risk of future compromise. In 2024, NIST formally released a new series of PQC standards, representing not only a significant technological evolution in cryptography, but also a clear signal for structural transformation across the global semiconductor industry.
In particular, the LMS and XMSS algorithms specified in SP 800-208, recognized for their high security assurance and maturity, are widely regarded as critical technologies for secure firmware updates in long-lifecycle devices such as industrial control systems, automotive electronics, and server baseboard management controllers (BMCs). Meanwhile, FIPS 205 provides stateless hash-based signatures, offering a flexible and complementary option for a wide range of application scenarios.
Charles Hsu, founder, eMemory and PUFsecurity, stated: “Achieving full NIST certification across FIPS 203, 204, 205, and SP 800-208 represents a major milestone for eMemory and PUFsecurity in the field of hardware security. Under the growing shadow of ‘harvest-now, decrypt-later’ threats, compliance has become an urgent industry imperative. Our comprehensive certification portfolio not only addresses today’s security compliance requirements, but also enables our partners to establish robust and future-proof defenses well ahead of the commercialization of quantum computers.”
Hardware Root of Trust: Cornerstone of PQC Security
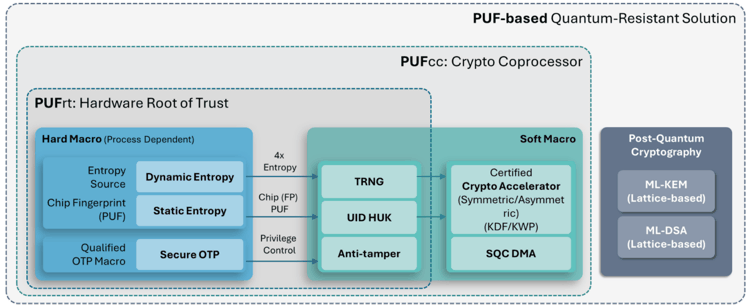
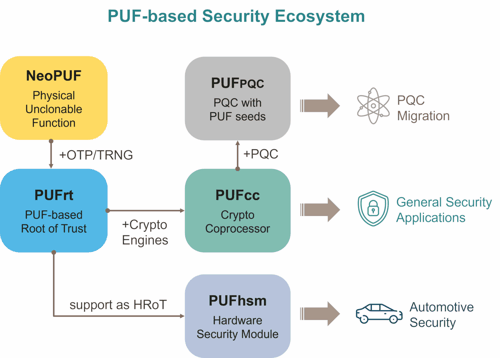 While PQC algorithms provide mathematical resistance against quantum attacks, their real-world security ultimately depends on the quality of key generation and storage. Without sufficient randomness at the source or robust protection of stored keys, even the strongest algorithms can be rendered ineffective. eMemory and PUFsecurity emphasize that the core strength of PUF-PQC lies in its deep integration with PUFrt (Root of Trust), addressing the most critical challenges in PQC implementation at the physical level:
While PQC algorithms provide mathematical resistance against quantum attacks, their real-world security ultimately depends on the quality of key generation and storage. Without sufficient randomness at the source or robust protection of stored keys, even the strongest algorithms can be rendered ineffective. eMemory and PUFsecurity emphasize that the core strength of PUF-PQC lies in its deep integration with PUFrt (Root of Trust), addressing the most critical challenges in PQC implementation at the physical level:
-
NeoPUF (Physical Unclonable Function, silicon fingerprint):
Leverages inherent manufacturing variations to generate chip-unique identities, serving as the entropy foundation for all cryptographic key generation and ensuring keys are unclonable and tamper-resistant -
TRNG (True Random Number Generator, entropy source):
Delivers high-quality, NIST-compliant physical entropy, ensuring the unpredictability required for PQC algorithms -
NeoFuse OTP (One-Time Programmable Memory, secure storage):
Provides highly reliable NVM for secure storage of sensitive data and cryptographic material, establishing a complete and trusted chain of security
Building Sustainable Quantum-Secure Ecosystem for Future
The newly certified FIPS 205 and SP 800-208 standards are particularly well suited for mission-critical infrastructure that demands the highest security assurance and long-term maintainability. LMS-based signatures, built entirely on hash functions, are widely regarded as among the most robust digital signature schemes against quantum attacks, making them ideal for verifying firmware authenticity and preventing malicious code injection.
Michael Ho, president, eMemory Technology, added: “Our solution is not merely a collection of certified IP blocks – it represents a scalable and sustainable trust architecture for the post-quantum era. By combining eMemory’s long-standing technical and production expertise in embedded memory with PUFsecurity’s specialization in hardware security design, we significantly lower the barrier to PQC adoption. Chip designers can integrate these NIST-validated modules into their designs without needing deep expertise in complex cryptographic parameters.”
The fully NIST-certified PUF-PQC solution is now commercially available and can be integrated across both advanced and mature process platforms at multiple foundries. From cost-sensitive IoT endpoint devices to HPC and AI accelerators, PUF-PQC enables customers to build robust security architectures while complying with stringent international security frameworks such as CNSA 2.0 (the post-quantum cryptography migration framework), confidently guiding the industry into the post-quantum era.










 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter


