CES 2026: How Ephemeral AI Storage Saves Cost and Increases AI Performance
Required by ever demanding AI needs
By Philippe Nicolas | January 7, 2026 at 2:00 pmBlog written by Neil Stobart, CTO, Cloudian published Jan 5, 2026
At CES, Nvidia announced Nvidia BlueField-4-powered Inference Context Memory Storage Platform validates what forward-thinking AI architects have long understood: AI inference is creating a new class of data that doesn’t need traditional fault-tolerant storage – and treating it like permanent data is costing AI-native organizations billions in unnecessary infrastructure.
The reason is the KV Cache. When large language models process text, they compute Key and Value vectors for each token to determine relationships between words. Without caching, generating each new token would require recalculating these vectors across the entire input – a process that scales quadratically with context length. The KV Cache stores these vectors for reuse, and as context windows expand to hundreds of thousands of tokens, cache sizes have grown to tens of gigabytes per session, often exceeding GPU memory.
But here’s the critical insight: KV Cache is derived entirely from source documents that remain protected in fault-tolerant storage. If cached data is lost, it can be regenerated. This recomputability enables a new storage architecture – Ephemeral AI Storage (EAS) – that eliminates redundancy overhead in favor of performance and cost efficiency.
The Persistence Mandate in Traditional Storage
Enterprise storage has always been defined by the persistence mandate: data must be protected against all foreseeable hardware failures and corruption, including ransomware. This is enforced through data redundancy techniques such as RAID and erasure coding, which distribute data parity information to reconstruct lost blocks, plus backup, recovery, immutability, and replication technologies.
In AI applications, this mandate applies to:
- Source Data: Training datasets, source documents, and internal knowledge bases
- Operational Data: User prompts, inference logs, and final system responses
These assets are non-negotiably stored in non-volatile, fault-tolerant storage to prevent irrecoverable loss of business data or intellectual property.
The Emergence of Ephemeral AI Data
Modern LLMs and other AI systems generate substantial amounts of intermediate data that significantly accelerate subsequent operations. A primary example is the KV cache.
The KV cache stores the pre-computed attention keys and values for input tokens. This cache is used to accelerate multi-turn conversations (chat history) or cross-user inference on commonly used documents. When a document is ingested, its attention vectors are computed once and stored as a KV cache, where they can be reused for subsequent queries.
As prompts get longer, the size of the KV cache grows linearly but the amount of compute effort needed to recalculate it grows quadratically. Agentic AI conversations, RAG, and research models are making inference prompts longer, into the hundreds of thousands of tokens, resulting in KV cache sizes up to 80GB or more for a single conversation. The context for multiple conversations will no longer fit in GPU or even CPU/system memory and must be kept on shared storage to avoid constantly recomputing the KV cache.
The Recomputability Principle
Critically, the KV cache represents pre-computed, ingestible data. It is produced solely from the original, secured source data (e.g., the base document). Therefore, if a KV cache entry is lost due to a storage failure, it can be regenerated immediately by re-running the ingest and pre-computation process on the source document.
This recomputability principle fundamentally changes the storage requirement. The KV cache does not require the strict fault tolerance and permanence of the underlying source data.
EAS Characteristics
EAS must deliver fast sequential read performance, meaning high throughput and low latency. Write performance does not need to be as fast as read performance, because reading KV cache affects inference response time but writing KV cache does not. The faster the GPU servers can read KV cache, the faster they can produce the first token of the response (time to first token, or TTFT).
EAS must offer shared read access so multiple GPU servers can read the KV cache, but shared writes to the same KV cache is not necessary, as KV cache is never modified once written, only read or deleted. EAS must also offer good write media endurance because new KV cache data will be written frequently.
EAS Benefits
By eliminating the necessity for complex, hardware-intensive fault tolerance mechanisms (like multi-copy replication or erasure coding), a new storage class – Ephemeral AI Storage – can prioritize speed and density over resilience.
- Cost Reduction: Removing redundant storage overhead (typically 2x to 3x data capacity for fault tolerance) drastically lowers TCO
- Performance Improvement: Write and read paths are simplified, as the system does not need to compute or reconcile parity data, leading to lower latency and higher IOPS, which is essential for fast inference and cache warm-up
In summary, the KV cache and similar intermediate AI artifacts represent a paradigm shift, justifying a purpose-built storage class that acknowledges and embraces the risk of data loss in favor of architectural and economic efficiency.
Nvidia BlueField-4 and the Inference Context Memory Storage Platform
At CES, Nvidia announced the Nvidia Rubin platform featuring BlueField-4-powered Inference Context Memory Storage Platform, a new class of AI-native storage infrastructure purpose-built for the ephemeral data challenges described above. It treats KV cache as a first-class data type, storing and distributing it across agentic workflows without the overhead of traditional fault-tolerant storage. Enabled by Nvidia Spectrum-X Ethernet, extended context memory for multi-turn AI agents improves responsiveness, increases throughput per GPU and supports efficient scaling of agentic inference.
By extending effective GPU KV cache capacity and enabling high-bandwidth sharing of context across the AI pod, The platform delivers superior power efficiency, 6x higher than traditional storage solutions. This validates the ephemeral storage architecture: When data is recomputable, infrastructure should optimize for speed and efficiency rather than redundancy. Its integration with Nvidia Spectrum-X Ethernet, Nvidia DOCA and Nvidia Dynamo enables AI-native organizations to scale inference services efficiently while reclaiming essential power for gigascale AI.
Cloudian delivers both classes of AI Storage
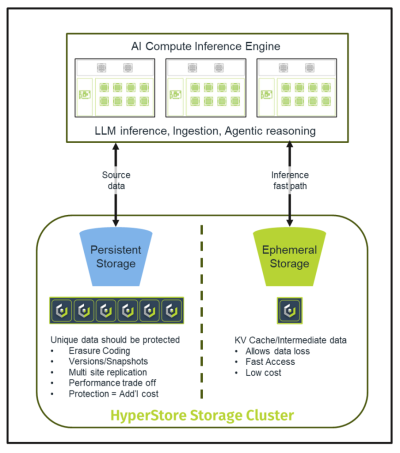
Cloudian HyperStore supports both classes of AI storage, traditional and ephemeral, by simple storage policy configuration applied at the storage tenant level. Protected data can use adjustable replica copies or erasure coding algorithms for data protection and redundancy. The protection parity levels can be increased to provide more protection for source documents, vector databases, or logs, or decreased when minimal or no persistence guarantees are needed, such as for KV cache.
One cluster can support both persistent and ephemeral storage simultaneously. HyperStore can also configure different storage spaces on different media types to optimize for the appropriate workload whether it’s to minimize cost, maximize performance or provide data integrity and persistence with data protection.
Built on the foundations of S3 over RDMA, HyperStore can inject data directly from the storage platform into GPU memory at extreme high speeds providing a platform that effectively extends the AI context memory into limitless capacity, hugely reducing compute cost and enabling the performance required for long context queries.










 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter


