Kioxia Develops Core Technology that Will Allow Practical Implementation of High-density, Low-power 3D DRAM
Was presented at IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) held in San Francisco, CA, USA
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on December 18, 2025 at 2:00 pmKioxia Corporation announced the development of highly stackable oxide-semiconductor channel transistors that will enable the practical implementation of high-density, low-power 3D DRAM.
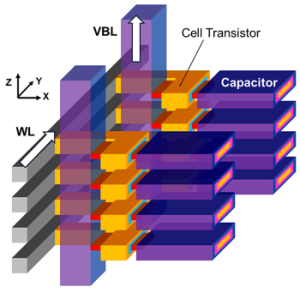
3D OCTRAM cell structure
This technology was presented at the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) held in San Francisco, CA, USA, on December 10, and has the potential to reduce power consumption across a wide range of applications, including AI servers and IoT components. (*)
In the era of AI, there is growing demand for DRAM with larger capacity and lower power consumption that can process large amounts of data. Traditional DRAM technology is reaching the physical limits of memory cell size scaling, prompting research into the 3D stacking of memory cells to provide additional capacity. The use of single-crystal silicon as the channel material for transistors in stacked memory cells, as is the case with conventional DRAM, drives up manufacturing costs, and the power required to refresh the memory cells increases proportionally to the memory capacity.
Electrical characteristics of oxide-semiconductor horizontal transistors
At last year’s IEDM, Kioxia announced the development of Oxide-Semiconductor Channel Transistor DRAM (OCTRAM) technology that uses vertical transistors made of oxide-semiconductors. In this year’s presentation, we showcased technology of highly stackable oxide-semiconductor channel transistors allowing 3D stacking of OCTRAM, verifying the operation of transistors stacked in 8 layers.
Cross-sectional TEM image of 8-layer oxide-semiconductor horizontal transistor
This new technology stacks mature silicon-oxide and silicon-nitride films and replaces the silicon-nitride region with an oxide-semiconductor (InGaZnO) to simultaneously form vertical layers of horizontally-stacked transistors. Kioxia have also introduced a novel 3D memory cell structure capable of scaling the vertical pitch. These manufacturing processes and structures are expected to overcome the cost challenges of achieving 3D stacking of memory cells.
Additionally, it is expected that the refresh power can be reduced thanks to the low off-current characteristics of oxide-semiconductors. Kioxia have demonstrated high on-current (more than 30μA) and ultra-low off-current (less than 1aA, 10^-18A) capabilities for the horizontal transistors formed by the replacement process. Moreover, the company have successfully fabricated an 8-layer stack of horizontal transistors and confirmed the successful operation of the transistors within that structure.
The firm will continue R&D of this technology in order to realize the deployment of 3D DRAM in real-world applications.
(*) This announcement has been prepared to provide information on our business and does not constitute or form part of an offer or invitation to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy or subscribe for or otherwise acquire any securities in any jurisdiction or an inducement to engage in investment activity nor shall it form the basis of or be relied on in connection with any contract thereof.










 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter


