First increase in Ransomware Attacks in Three Years Driven by New Technology
Insights from IT and Security professionals on ransomware attacks, attack vectors, response & awareness
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on October 20, 2025 at 2:00 pmSummary:
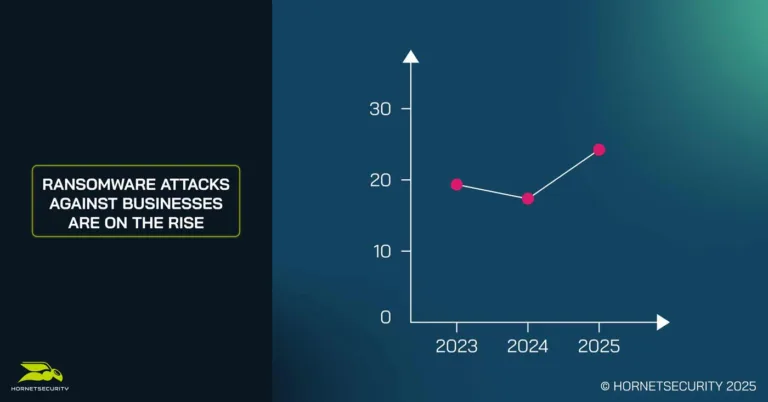
- Ransomware attacks affected 24% of organizations in 2025, up from 18.6% in 2024
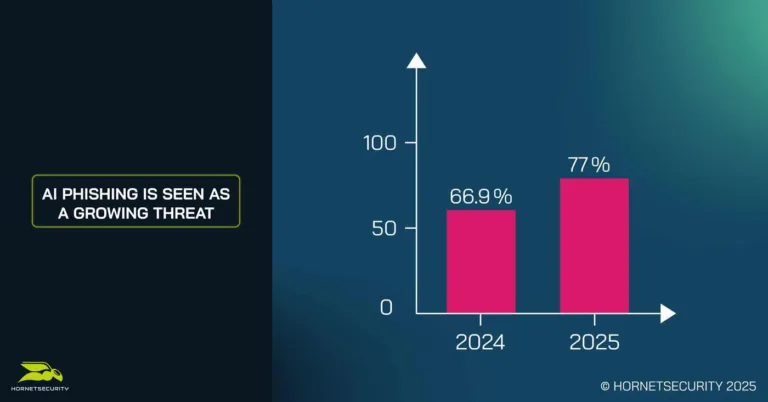
- 77% of CISOs see AI-powered phishing as a real and emerging threat
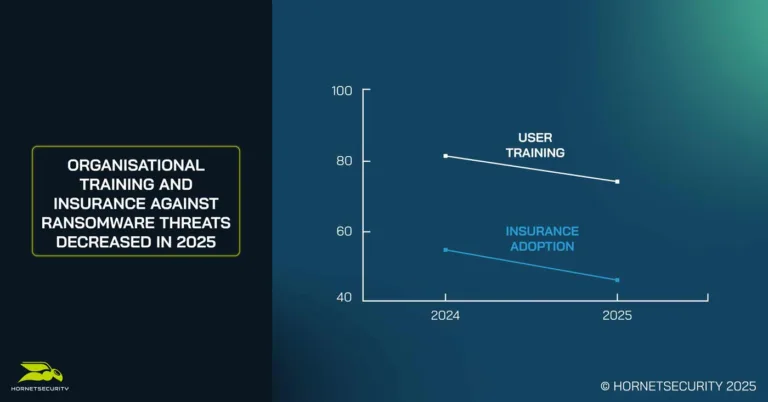
- Only 46% of organizations have ransomware insurance, down from 54.6% in 2024
New research from leading cybersecurity provider Hornetsecurity has found that a quarter (24%) of businesses reported being victims of a ransomware attack in 2025, a sharp increase from 18.6% in 2024. The results from Hornetsecurity’s annual Ransomware Impact Report mark the end of a multi-year decline in attacks.
The rise comes as cybercriminals continue to diversify their methods and leverage new technologies to bypass defences. While traditional phishing remains the leading attack vector in nearly half of attacks (46%), the report finds that a growing reliance on compromised endpoints (26%) and stolen credentials (25%) are increasingly common access vectors.
While attacks are increasing, the number of organizations investing in ransomware insurance is down year on year, with less than half of all businesses (46%) making sure they are insured against these attacks, compared to 54.6% last year.
“Following a multi-year decline in ransomware attacks, 2025 marks a critical turning point for organizations to strengthen their security against faster, smarter, and AI-automated ransomware attacks,” said Daniel Hofmann, CEO, Hornetsecurity. “It is concerning to see a reduction in businesses investing in ransomware insurance while attacks are on the rise. It’s worth noting, however, that it has become more difficult than ever for businesses to procure insurance for these situations. While hackers continue to use a wider variety of tactics, it’s clear that organizations must increase their security provisions if they are to succeed against these nefarious actors. For example, next-gen email security solutions are effective in keeping threats from reaching inboxes, while security awareness solutions help end-users spot more advanced threats like social engineering. Pair those with immutable backup storage and you have an effective strategy for guarding critical data against ransomware. These tools are effective whether the business is insured for ransomware or not.”
Businesses are reacting to the growing threat of AI-powered attacks
The study showed an overall reduction in phishing attacks over the past 12 months (52.3% in 2024 vs 46% in 2025). However, the increase in the use of AI-generated phishing was identified by over three quarters of CISOs (77%) as a growing threat.
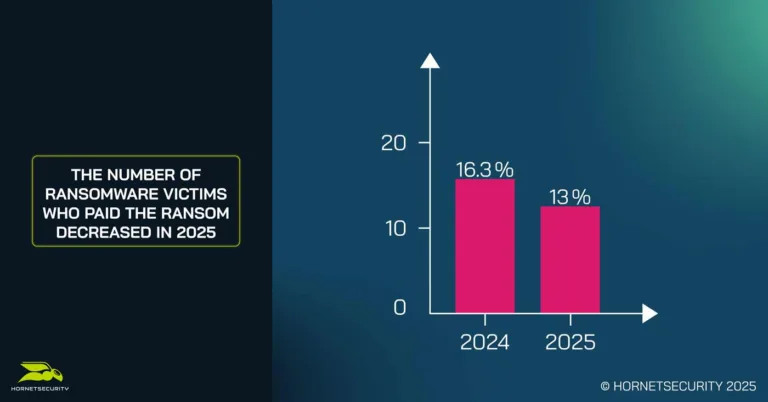
Despite new and emerging challenges, preparations and improvements in recovery capabilities appear to be paying off, with the proportion of victims paying ransoms at 13% compared to 16.3% in 2024. Improved preparedness has become standard, as 82% of organizations surveyed now have a Disaster Recovery Plan, and 62% utilize immutable backups.
Check-box training against AI-phishing is ineffective
While the research showed positive actions from businesses when it came to certain cybersecurity provisions, cybersecurity training is shown to still be lacking. While three quarters (74%) of organizations reported offering end-user training against ransomware attacks, over two fifths of security leaders (42%) admitted that their training was insufficient or ineffective.
The report discusses the growing issue among small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) of “false compliance”. This occurs when organizations meet a superficial level of cybersecurity awareness, often through check-box training, but lack adequate follow-up. This contributes to ongoing human error, particularly when sophisticated phishing and social engineering tactics are employed.
Leadership & Governance: Still Catching Up
According to Proofpoint, that recently announced its planned acquisition of Hornetsecurity, human error remains the dominant source of incidents: 66% of CISOs identify the human factor as the primary attack vector, particularly in terms of data leaks and internal compromise. Although training is improving, it often remains superficial (42% consider it inadequate). These findings corroborate Hornetsecurity’s conclusions on the limitations of “compliance tick-box” programs.
“To be effective, cybersecurity awareness training must be ongoing, relevant, and tailored to each individual, which is only realistically possible if it is automated by a next-gen, AI-powered solution such as our Security Awareness Service,” continued Hofmann. “While it is heartening to see a decrease in ransom payments, there can be no room for complacency. The new standard for businesses in fighting against ransomware is to deploy a comprehensive cyber-defence which not only protects against initial breaches, but also acts to prevent future threats, and ensures resilient systems capable of swift recovery if incidents do occur.”
To access the report click here.













 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

