Storj Report: Distributed Cloud Storage Reduces Carbon Emissions by Up to 83% Compared to Other Providers Over 3-Year Period
Report assessed carbon costs of cloud storage, including powering drives and data centers, and manufacturing, transport, and end-of-life phases of drive’s life cycle to develop model to estimate carbon savings.
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on July 5, 2023 at 2:02 pmSummary:
- Sustainability report assessed the carbon costs of cloud storage, including powering drives and data centers, and the manufacturing, transport, and end-of-life phases of a drive’s life cycle to develop a model to estimate carbon savings.
- Model found that Storj’s distributed approach, which harvests unused capacity in drives that are already manufactured, powered, and cooled for other purposes, produces carbon savings of up to 83% per terabyte of data.
- Findings indicate firm’s distributed cloud storage model is a viable alternative to hyperscalers in reducing the industry’s environmental footprint while providing high-performance, globally reliable, secure, enterprise-grade cloud storage – all at a 1/10 of the cost.
Storj released the findings from its sustainability whitepaper on the environmental impact of cloud storage.
The report, produced by the company’s team and reviewed by academic researchers, identifies the carbon costs of traditional cloud storage in centralized data centers and presents a model to estimate carbon savings from using Storj compared to hyperscaler and centralized clouds.
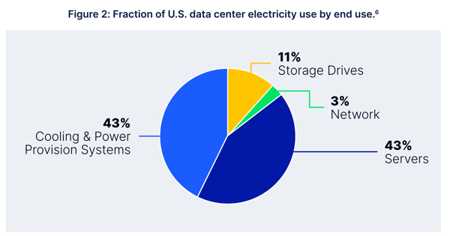
The demand for cloud storage is growing, as is the need for reliable, secure, and performant cloud storage. The rise of AI, which requires large datasets for machine learning, is exacerbating the problem. Centralized providers like Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud rely on expanding data centers, which account for 3% of all electricity generated on Earth. According to Greenly, storage centers are responsible for 2% of global carbon emissions when you include all devices that make use of storage.
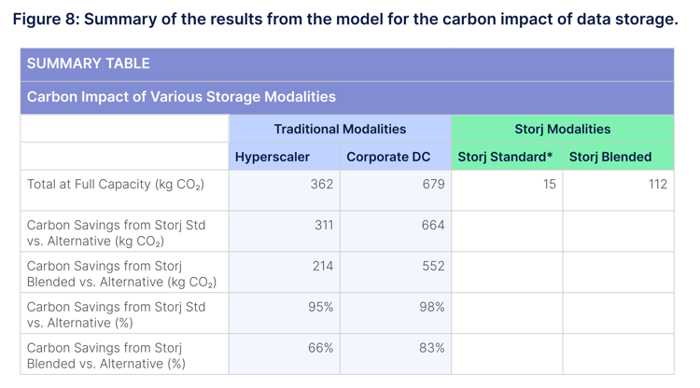
“When assessing the environmental impact of centralized providers, it’s essential to consider not only the electricity generated in powering and cooling data storage devices but the environmental impact from manufacturing and transporting those devices as well,” said JT Olio, chief architect, Storj. “Storj is able to eliminate much of those costs by storing data on the under-utilized capacity of drives that are already manufactured, powered, and cooled for other purposes. Through our analysis, we estimate that per terabyte of data, Storj’s distributed model reduced the carbon footprint of storing a terabyte of data by 66-83% over a 3-year period compared to other providers.”
Report outlines significant carbon savings are additionally achieved by:
1. Extending the effective life of already manufactured drives.
2. Minimizing the number of copies of data that need to be stored to achieve equivalent data durability, global distribution, and performance levels.
3. Enabling a carbon-efficient distribution of storage between HDDs and SSDs.
The company leverages the underutilized storage capacity from over 24,000 nodes independently operated worldwide. 80% of HDDs WW are only 20% full; by leveraging this existing capacity, Storj eliminates the need to build new drives and data centers, while alleviating the need for incremental electricity and cooling. The distributed architecture is also designed to protect vs. outages, ransomware, and data compromise while boosting performance and reliability.
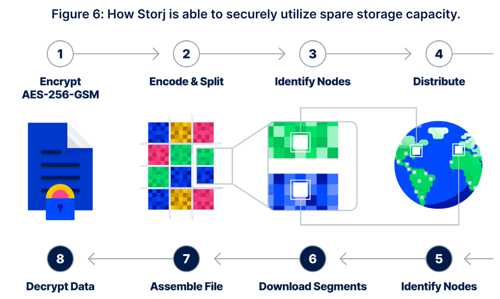
“We understand that customers have traditionally had to prioritize performance and cost first, sustainability second,” said Ben Golub, CEO, Storj. “Storj is proud to lead the trend where a sustainable solution doesn’t compromise performance and in fact can be 90% less expensive than leading cloud object storage providers. What we’ve done at Storj is leverage a distributed model to create a truly viable alternative to hyperscalers that is not only more cost-effective and sustainable but outperforms centralized platforms in performance, security, and reliability.”
Full report on sustainability (registration required)















 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

