From AWS, Replication for Amazon Elastic File System
Allows EC2 instances, AWS Lambda functions, and containers to share access to fully-managed file system.
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on February 3, 2022 at 2:02 pm By Jeff Barr, chief evangelist, AWS (Amazon Web Services)
By Jeff Barr, chief evangelist, AWS (Amazon Web Services)
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) allows EC2 instances, AWS Lambda functions, and containers to share access to a fully-managed file system.
First announced in 2015 and generally available in 2016, Amazon EFS delivers low-latency performance for a variety of workloads and can scale to thousands of concurrent clients or connections. Since the 2016 launch, we have continued to listen and to innovate, and have added new features and capabilities in response to feedback. These include on-premises access via Direct Connect (2016), encryption of data at rest (2017), provisioned throughput and encryption of data in transit (2018), an infrequent access storage class (2019), IAM authorization and access points (2020), lower-cost one zone storage classes (2021), and more.
Introducing replication
Today the company announces that you can now use replication to automatically maintain copies of your EFS file systems for BC or to help you to meet compliance requirements as part of your DR strategy. You can set this up in minutes for new or existing EFS file systems, with replication either within a single AWS region or between 2 AWS regions in the same AWS partition.
Once configured, replication begins immediately. All replication traffic stays on the AWS global backbone, and most changes are replicated within a minute, with an overall RPO of 15mn for most file systems. Replication does not consume any burst credits and it does not count against the provisioned throughput of the file system.
Configuring Replication
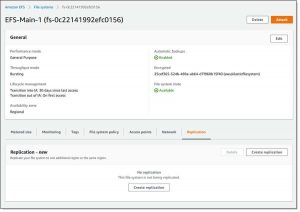
To configure replication, open the Amazon EFS Console , view the file system that you want to replicate, and select the Replication tab:
Click to enlarge
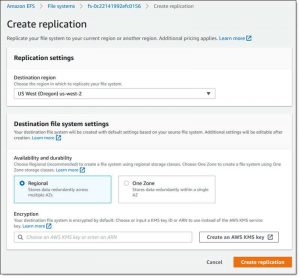
Click Create replication, choose the desired destination region, and select the desired storage (Regional or One Zone). You can use the default KMS key for encryption or I can choose another one. Review your settings and click Create replication to proceed:
Click to enlarge
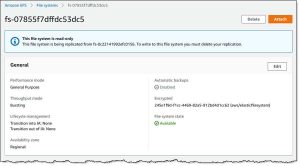
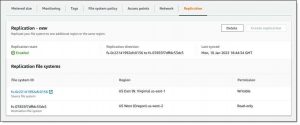
Replication begins right away and you can see the new, read-only file system immediately:
Click to enlarge
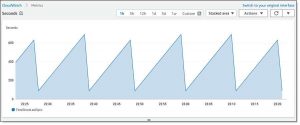
A new CloudWatch metric, TimeSinceLastSync, is published when the initial replication is complete, and periodically after that:
Click to enlarge
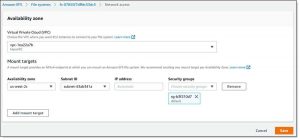
The replica is created in the selected region. Iyou create any necessary mount targets and mount the replica on an EC2 instance:
Click to enlarge
EFS tracks modifications to the blocks (currently 4MB) that are used to store files and metadata, and replicates the changes at a rate of up to 300MB/s. Because replication is block-based, it is not crash-consistent; if you need crash-consistency you may want to take a look at AWS Backup.
After having set up replication, you can change the lifecycle management, intelligent tiering, throughput mode, and automatic backup setting for the destination file system. The performance mode is chosen when the file system is created, and cannot be changed.
Initiating a Fail-Over
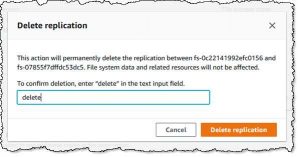
If you need to fail over to the replica, you simply delete the replication. You can do this from either side (source or destination), by clicking Delete and confirming your intent:
Click to enlarge
You enterdelete, and click Delete replication to proceed:
Click to enlarge
The former read-only replica is now a writable file system that you can use as part of your recovery process. To fail-back, you create a replica in the original location, wait for replication to finish, and delete the replication.
You can also use the command line and the EFS APIs to manage replication.
For example:
-
create-replication-configuration/CreateReplicationConfiguration– Establish replication for an existing file system. -
describe-replication-configurations/DescribeReplicationConfigurations– See the replication configuration for a source or destination file system, or for all replication configurations in an AWS account. The data returned for a destination file system also includesLastReplicatedTimestamp, the time of the last successful sync. -
delete-replication-configuration/DeleteReplicationConfiguration– End replication for a file system.
Available
This new feature is available and you can start using it today in the AWS US East (N. Virginia), US East (Ohio), US West (N. California), US West (Oregon), Asia Pacific (Mumbai, India), Asia Pacific (Osaka, Japan), Asia Pacific (Seoul, Korea), Asia Pacific (Singapore), Asia Pacific (Sydney, Australia), Asia Pacific (Tokyo, Japan), Canada (Central), Europe (Frankfurt, Germany), Europe (Ireland), Europe (London, UK), Europe (Paris, France), Europe (Stockholm, Sweden), South America (São Paulo, Brazil), and GovCloud Regions.
You pay the usual storage fees for the original and replica file systems and any applicable cross-region or intra-region data transfer charges.













 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

