History (1994): Sony Developed “Metal Servo Micro Floppy Disk”
21MB diskette to counterattack 21MB Floptical from Insite Peripherals
By Jean Jacques Maleval | December 23, 2020 at 2:35 pmSony of Japan has developed the “Metal Servo Micro Floppy Disk”, a new diskette with a 21MB formatted capacity (28.1MB unformatted) on a single 3.5-inch disk.
“Sony invented the 3.5-inch micro floppy disk in 1980, and over the last decade, we have shown our commitment to the format through a variety of product line extensions and enhancements,” said Art Rancis, VP data media products, Sony recording media products group. “Today we have responded to market demands for larger capacity micro floppy disks with the development of a 21MB model.“
Metal servo drives maintain R/W downward compatibility with conventional disk drives (0.72, 1.44 and 10MB diskettes from NEC).
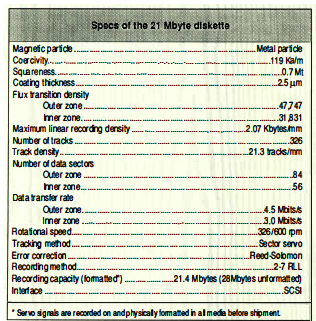
The new disks are developed with Sony’s advanced metal magnetic particle technology previously applied to 8mm video and 4mm DAT audio metal tapes and D8 and DDS data cartridges. Metal servo micro floppy disks have 3x the linear density and 4x the track density of conventional double-sided high density disks.
This is primarily made possible by the application of 2 new technologies: “Metal magnetic particle technology” and “Sector servo tracking technology.” Metal servo is named after these technologies. In addition, 2 other technologies, ZBR and 2-7 RLL are applied to this format. ZBR allows the storage of data on the outer portion of a disk more efficiently, while 2-7 RLL coding increases the linear density of data encoding.
In the manufacturing of microfloppy disks, a specialized coating process is used to make the disk’s surface smoother, which in turn increases the stability and output of the disk. The disk is coated with magnetic metal particles to a thickness of 2.5 microns with a newly-developed binder system, which increases the strength of the disk, as well as the density of the data stored. In order to read the disk, the magnetic head traces a servo signal encoded on the disk during the manufacturing process. The sector servo technology used in the new format helps the magnetic head follow the tracks where the data is stored on the disk, thereby enabling readout of higher density data.
Sony’s Metal servo super high density disk was designed according to the specs proposed by the Japan Electronic Industry Development Association (JEIDA) and supported by NEC, Sony, Mitsubishi, Canon, Teac and Teijin.
NEC developed the first drive and Sony the first disk.
The new format is scheduled to be published as a Japanese industrial standard. Metal servo micro floppy disks will be recognized as an International Standard for high density FDDs in 1994, said Sony.
The operation’s aim is obviously to counterattack the 21MB Floptical from Insite Peripherals that formed a Floptical Technology Association (Cupertino,CA) in which are involved 3 Japanese: Chinon, Hitachi Maxell and MKE.
This article is an abstract of news published on the former paper version of Computer Data Storage Newsletter on issue 72, published on January 1994.














 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

