Symphonic Cooperative Flash Zones for SSD From Radian Memory Systems
SSDs to provide flash zones, zone tiering, and an 'All Firmware' SDF implementation
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on February 22, 2019 at 2:22 pmRadian Memory Systems, Inc. brings’ Flash zones’ to data center storage with the release of its Symphonic Cooperative Zones technology available on its RMS-350 U.2 SSD and RMS-325 edge card SSD.
Based upon the company’s technology, Symphonic Cooperative Zoned SSDs include several industry milestones, including being SSDs to provide flash zones, zone tiering, and an ‘All Firmware’ SDF implementation.
Symphonic Cooperative Flash Zones:
-
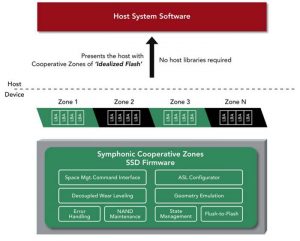
Cooperative Zones Symphonic Cooperative Zones are contiguous logical blocks of ‘Idealized Flash’ that come from the same physically isolated regions of memory and can be associated with namespaces. Configurable in capacity, flash management of these zones is performed by the SSD under cooperative host control.
-
Zone tiering SSDs can be factory configured with different zones supporting different memory types (e.g., SLC, TLC, and NV-RAM today, and SCM or QLC in the future).
-
‘All-Firmware’ SDF SSD Symphonic ‘Idealized Flash’ and ‘Configurable Addressing’ are completely in SSD firmware. No host libraries are required for log structured hosts, making the SSD less OS dependent and optimal for SPDK applications.
Radian RMS-350 SSD
The company delivered first evaluation units of its Cooperative Zoned SSDs to OEM customers over a year ago, in January 2018. Available on the firm’s NVMe 2.5″ U.2 RMS-350 SSD and RMS-325 HHHL edge card SSD, Symphonic Cooperative Zones bring configurable and deterministic flash zones to storage applications throughout the data center. For use in storage arrays, hyperconverged appliances, and SDS frameworks, Cooperative Zones can minimize write amplification while providing maximum parallelization and I/O isolation. The result is better tail latencies, bandwidth, overprovisioning and endurance than found with conventional FTL based SSDs.
SSD RMS-325
The firm’s publicly introduced the industry to the concept of flash zones in September 2015, at the SNIA annual Storage Developer’s Conference (SDC) held in Santa Clara, CA. Providing a talk titled Integrating Cooperative Flash Management with SMR Technology for Optimized Tiering in Hybrid Systems, the company illustrated how its Cooperative Flash Management (CFM) technology could enable flash zones, and use SMR commands and tiering to more deterministically and efficiently perform SSD flash management.
Problem statement
Conventional SSDs with embedded Flash-Translation-Layers (FTLs) perform flash management processes (garbage collection, wear leveling, and NAND maintenance) asynchronously, when the SSD autonomously deems necessary. This black box approach leads to unpredictable performance and latency spikes that can only be mitigated with overprovisioning. More recent workarounds propose achieving determinism by turning off I/O access to large portions of the SSD for periods of time. But this approach is impractical for most systems without employing even more overprovisioning.
Cooperative zones
Symphonic Cooperative Zoned SSDs present the host with idealized, configurable flash zones that can be associated with namespaces. It are comprised of NAND Erase Units (blocks) that are subsets of the same physically isolated region of memory and are configurable in size. Zones are accessible via conventional Logical Block Addressing (LBA) through the NVMe command set. Certain SMR zone commands, such as Zone Report and Zone Reset, are supported as part of extensions to the conventional NVMe command set.
Accessing a Symphonic Cooperative Zoned SSD follows the same host/device model as earlier Symphonic SSDs. This enables the host to control data placement while the SSD abstracts lower level media management, including geometry and vendor-specific NAND attributes (‘Idealized Flash’). Flash management processes such as garbage collection, wear leveling, and NAND maintenance are executed by the device, under cooperative host control, and hence performed deterministically.
Tiered zones
Symphonic Cooperative Zones offer a simple, logical model to access different memory types as different zones on the same SSD, from NV-RAM to storage class memory to NAND flash, and different classes of NAND flash. Variations of SLC NAND can provide very low latency and high endurance, while TLC NAND provides better capacity and cost efficiencies. The architecture can support factory configured zones designated as SLC, or TLC, or NV-RAM zones today, and other memory types such as QLC, SCM, and specialized ultra low latency SLC variations in the future. Combined with the company’s Delegated-Copy Move technology, this enables hosts to readily apply tiering between zones based upon different memory technologies to optimize efficiency trade-offs for cost, performance, capacity and endurance.
First ‘all firmware’ SDF SSD
Until now, Software-Defined Flash (SDF) SSDs have either not offered ‘Idealized Flash’ or ‘Configurable Addressing,’ or, in the case of the company’s SDF SSDs, required proprietary host resident libraries to provide this functionality. Symphonic Cooperative Zoned SSDs are the first SDF SSDs to provide this functionality in device firmware, without requiring any host libraries. This obviates the issues of having to integrate proprietary vendor libraries into host system software and minimizes OS compatibility requirements. The ‘All Firmware’ implementation is especially advantageous in SPDK environments which do not require NVMe device drivers or use of the kernel block layer, as existing targets can access the Cooperative Zoned SSDs directly without transitioning through intermediary libraries.
ZBD to NVMe bridge
The company offers an optional host library to customers already using the zone block device (ZBD) interface. Providing a protocol translation from the zone block device interface to NVMe, this bridge enables system software to access the Symphonic Cooperative Zoned SSD as a NVMe block device using a subset of the SMR zone block device commands.
Symphonic Cooperative Flash Zone configurations of the company’s RMS-350 U.2 SSD and RMS-325 HHHL SSD are available to cloud providers and system OEMs.
Read also:
FMS: Radian Memory Systems Unveils RMS-350 Open-Channel 2 Compliant Up to 12TB U.2 SSD
Includes support for Cooperative Flash Management based on Symphonic CFM technology, targeting AFAs, hyperconverged systems and cloud storage, offers highly parallelized, deterministic I/O while minimizing tail latencies for data center workload.
August 03, 2018 – Press Release















 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
