R&D: Near-Tc Ferromagnetic Resonance and Damping in FePt-Based HAMR Media
Data suggest that at temperatures 10–45K below Curie temperature, two-magnon scattering and spin-flip magnon-electron scattering make comparable contributions to ΔH.
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on January 8, 2019 at 2:11 pmPhysical Review Applied has published an article written by Daniel Richardson, Sidney Katz, Department of Physics, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado 80523, USA, J. Wang, Y. K. Takahashi, National Institute for Materials Science, Sengen 1-2-1, Tsukuba 305-0047, Japan, Kumar Srinivasan, Alan Kalitsov, Western Digital, San Jose, California 95131, USA, K. Hono, National Institute for Materials Science, Sengen 1-2-1, Tsukuba 305-0047, Japan, Antony Ajan, Western Digital, San Jose, California 95131, USA, and Mingzhong Wu,Department of Physics, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado 80523, USA.
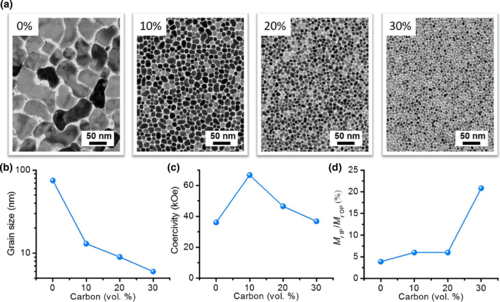
Figure 1 Microstructural and static magnetic properties of four FePt media samples.
(a) TEM images. (b) Average grain size as a function of the carbon-volume fraction (x).
(c) Coercivity as a function of x. (d) The ratio of in-plane remnant magnetization (Mr IP) to
out-of-plane remnant magnetization (Mr OP) as a function of x.
Abstract: “High-temperature ferromagnetic resonance (FMR) in FePt-based media materials is studied for the first time. The FMR linewidth (ΔH) as a function of temperature (T), field angle (θH), and the volume fraction (x) of carbon in the material is determined, and the effective Gilbert damping constant and the Bloch−Bloembergen relaxation time are estimated. The data suggest that at temperatures 10–45 K below the Curie temperature, two-magnon scattering and spin-flip magnon-electron scattering make comparable contributions to ΔH. With a decrease in T, ΔH increases due to enhancement of the two-magnon scattering. ΔH can be tuned via varying x and shows a maximum at θH≈45∘ when varying .“














 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

