R&D: Effects of Head Field and AC Field on Magnetization Reversal for MAMR
Investigated effects of head field and AC field on magnetization reversal using micromagnetic simulator
By Francis Pelletier | January 4, 2018 at 2:56 pmAIP Advances as published an article written by Aina Kase, Fumiko Akagi, Graduate School of Electrical Engineering and Electronics, Kogakuin University, Tokyo, Japan, and Kazuetsu Yoshida, Kogakuin University, Tokyo, Japan.
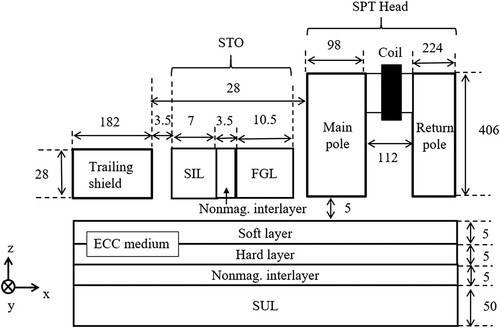
Shows a calculation model. The SPT head includes a main pole,
a return pole, and a trailing shield. The ECC medium consists of a soft and
a hard layer, a nonmagnetic interlayer, and a soft under layer (SUL).
The SPT head and the medium are divided into 7nm rectangular prism cells.
This size was a grain size in the medium. The STO is divided into 1.75nm
rectangular prism cells. Magnetization dynamic behavior was
calculated using a modified Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert equation
with a spin torque field (Hst)…
Abstract: “Microwave assisted magnetic recording (MAMR) is a promising recording method for achieving high recording densities in hard disk drives. In MAMR, the AC field from a spin-torque oscillator (STO) assists the head field with magnetization reversal in a medium. Therefore, the relationship between the head field and the AC field is very important. In this study, the effects of the head field and the AC field on magnetization reversal were analyzed using a micromagnetic simulator that takes the magnetic interactions between a single-pole type (SPT) write-head, an exchange coupled composite (ECC) medium, and the STO into account. As a result, the magnetization reversal was assisted not just by the y-component of the AC field (Hstoy) but also by the y-component of the head field (Hhy) in the medium. The Hhy over 100kA/m with a frequency of about 15.5GHz induced the magnetic resonance. The large Hhy was produced by the field from the STO to the SPT head.“













 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

