R&D: Blu-ray-Sensitive Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance for High-Density Optical Memory
Extending growth range of Ag NPs in volume of TiO2 to realize high-density optical memory
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on November 17, 2016 at 2:40 pmScientific Reports has published an article written by Shencheng Fu, Xintong Zhang, Qiang Han, Shuangyan Liu, Xiuxiu Han, and Yichun Liu, Center for Advanced Optoelectronic Functional Material Research, Northeast Normal University, and Key Laboratory of UV-Emitting Materials and Technology (Northeast Normal University), Ministry of Education, Changchun 130024, P. R. China
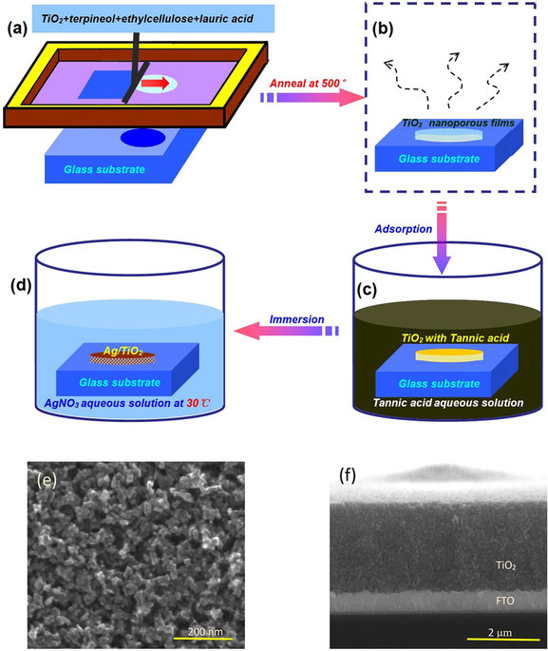
(a) TiO2 nanoporous films prepared on glass slides by a screen-printing method.
(b) Heat treatment to remove the polymer.
(c) Adsorption of TA on the surface of TiO2
(d) Thermal reduction of Ag nanoparticles in TiO2 nanoporous films.
(e) Top-view and (f) cross-section of SEM images of porous TiO2 films obtained
by screen-printing on the substrate of FTO.
Click to enlarge
Abstract: “Tunable spectrum-response is desired for efficient photo-energy transformation. Blu-ray (~405 nm) and polarization sensitive Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite films are thus fascinating in application of fast-response and high-density optical memory device. The Ag/TiO2 film has the ability of replicating hologram based on optical coherence by laser-stimulated dissolution of Ag nanoparticles (NPs). The rate and efficiency of the dissolution are supposed to be enhanced by introducing uniform and small-sized Ag NPs in TiO2 nanoporous films. However, no effective methods have been proposed to resolve this issue by now. Here, we develop a simple method of thermal-reduction to obtain high-density, space-dispersed and extremely small-sized Ag NPs in TiO2 nanoporous films pretreated with tannic acid. The film shows both high and narrow absorbance band centered at ~405 nm. Diffraction efficiency of the blu-ray holographic storage in the Ag/TiO2 film is improved by one order of magnitude compared to the traditional UV-reduced sample. Based on such properties, polarization-multiplexing holograms are able to be written at 405 nm and readout with little crosstalk. This work provides effective solutions for sensitizing localized surface plasmon resonance at near-UV region, extending the growth range of Ag NPs in the volume of TiO2, and resultantly, realizing high-density optical memory.”














 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

