Top 11 Reasons to Use Memory Channel Storage for SSDs – Diablo Technologies
Rather than PCIe
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on March 4, 2014 at 3:02 pmEnterprise storage has historically been hampered by technical and architectural factors that severely limit application performance. The I/O limitations of HDD-based arrays, and the latency imposed by PCI-Express based SSDs and architectures such as SAN and NAS, create bottlenecks for applications where speed and determinism are paramount.
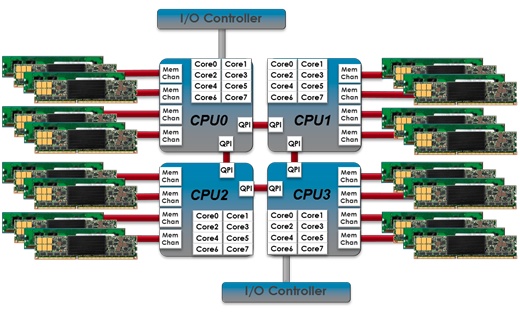
The emergence of solid state flash continues to disrupt the storage market with the recent introduction of Memory Channel Storage (MCS), a platform that delivers tens of terabytes of flash capacity in a single server with near-DRAM speeds. MCS technology puts NAND flash into a DIMM form factor and enables it to interface with the CPU via the integrated memory controller. The result is a new class of high-performance, in-memory storage that eliminates the OS/IO/network overhead inherent to legacy storage arrays.
Diablo Technologies, Inc., in memory system interface products and creator of the MCS architecture, offers eleven reasons to leverage this technology to optimize application performance for database, big data, virtualization, and low latency workloads.
- 1- Faster Data Persistence – It provides lower write latency than any other flash storage technology. Creating and updating persistent data is now faster than ever before with as low as 5?s write latency.
- 2- Zero-Compromise Performance – It eliminates the trade-off between IO/s and latency that is inherent to other flash storage solutions. Applications can now support heavy I/O while maintaining fast response times to ensure IT managers no longer need worry about tuning for just one of these performance attributes.
- 3- Predictable Response Times – It provides deterministic latency. Uncertainty surrounding storage-related Quality-of-Service (QoS) can now be eliminated. As an example, IT managers deploying VDI can be assured of consistent response times for VMs, providing their users with a satisfying session experience.
- 4- Scalability – The MCS architecture enables the flash storage solution to fit the customer requirements. I/O performance is linearly scalable and total capacity can be ‘right-sized’ to match application needs. Current products based on MCS are available as 200GB or 400GB modules. Multiple modules can be integrated into servers or storage arrays as needed, based on the capacity and performance requirements of specific applications.
- 5- Flexibility – Most data centers employ a variety of storage solutions depending on the challenges faced. Via its combined advantages (i.e. fast persistence, supports heavy I/O without compromising response time, determinism, scalability), MCS provides a flexible platform that can address a variety of workloads.
- 6- Mixed-Workload Performance – Due to its distributed architecture, it provides strong mixed-workload performance. Not only can MCS-based modules be written to or read from in parallel, but applications also have the flexibility to write to individual modules while reading from others. Mixed workload applications, such as databases and virtualized environments, benefit and are suited for MCS-based solutions.
- 7- Flexible Form Factor – By placing persistent memory on a standard DIMM module, MCS-based products will fit into any server or storage design that utilizes the standard DIMM form factor. Flash memory can be integrated into standard server and storage arrays with no modifications to the motherboards or chassis and without the complexity of blade servers requiring custom PCIe mezzanine cards. This makes MCS flexible means of deploying persistent memory for enterprise and storage applications.
- 8- Ecosystem Support – With support for the most critical OSs and hypervisors, MCS can be deployed quickly and easily into virtually any enterprise environment. Driver availability for Windows, VMware ESXi and the most prevalent Linux distributions and kernels means applicability to enterprise applications.
- 9- Memory Expansion – It redefines the idea of memory expansion by placing flash on the same memory channels as system DRAM. Paging occurs at near DRAM speeds as these operations are simply transfers of data from flash to DRAM within the same memory controller. No transfers through a storage stack or movements external to the processor are required, thereby enabling fast paging.
- 10- TCO – Each node in a cluster is able to complete more work in less time. With storage attached directly to the processors rather than across I/O expansion connections and storage stacks, data is accessed, manipulated, and rewritten to the flash in reduced time. Fewer nodes also means less external storage arrays filled with large amounts of hot, spinning media, and lower power and cooling costs that lead to a reduced TCO.
- 11- Future-Proof Platform – The MCS architecture is designed with the ability to utilize current NAND-flash as well as future non-volatile memories, ensuring MCS customers will benefit from the capacity and performance enhancements of technologies such as 3D flash, phase-change memory, magnetoresistive RAM, and resistive RAM.













 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

